When we think of The historical context of Shakespeare’s writing style, we often envision his powerful characters, gripping plots, and lyrical language. However, to truly appreciate the brilliance of Shakespeare’s writing, it’s essential to explore the historical context in which his works were created. The historical context of Shakespeare’s writing style backdrop of the Elizabethan era had a profound influence on Shakespeare’s writing style, from his use of language to the themes he explored. In this article, we will delve into how the historical context of Shakespeare’s writing style shaped his writing style, offering valuable insights into how this context influenced the depth and complexity of his characters and storytelling.
When we think of The historical context of Shakespeare’s writing style, we often envision his powerful characters, gripping plots, and lyrical language. However, to truly appreciate the brilliance of Shakespeare’s writing, it’s essential to explore the historical context in which his works were created. The historical context of Shakespeare’s writing style backdrop of the Elizabethan era had a profound influence on Shakespeare’s writing style, from his use of language to the themes he explored. In this article, we will delve into how the historical context of Shakespeare’s writing style shaped his writing style, offering valuable insights into how this context influenced the depth and complexity of his characters and storytelling.
By understanding The historical context of Shakespeare’s writing style forces that shaped Shakespeare’s work, we can uncover the layers of meaning that make his plays not just timeless, but a reflection of the society in which he lived.
The Elizabethan Era: A Snapshot

The Elizabethan era, spanning from 1558 to 1603, was a time of remarkable cultural and social transformation in England. Under the reign of Queen Elizabeth I, England saw a surge in artistic achievement, exploration, and political stability. This period, often referred to as the “Golden Age,” was marked by the flourishing of the arts, including theater, which played a central role in the lives of Elizabethans.
Shakespeare wrote during this time, and his works reflect the values, struggles, and concerns of an evolving society. Politically, England was navigating its relationship with Catholic Europe, as tensions rose from the Protestant Reformation. Socially, the rigid class structure was both a source of tension and inspiration for many of Shakespeare’s plays. Moreover, the rise of public theaters in London created a new kind of entertainment that shaped the way Shakespeare wrote—his plays were made to be performed, not just read.
This era’s blend of political upheaval, social change, and intellectual growth directly influenced Shakespeare’s writing style, infusing his works with themes of power, identity, and human nature. Understanding this historical backdrop allows us to better appreciate the depth and relevance of Shakespeare’s plays today.
The Influence of the Renaissance on Shakespeare’s Writing

The Renaissance, which began in Italy in the 14th century and spread throughout Europe, had a profound impact on England during the Elizabethan era. This cultural movement emphasized a renewed interest in classical knowledge, humanism, and the potential of the individual. Shakespeare was deeply influenced by these ideals, and they shaped his writing in significant ways.
One of the most notable aspects of the Renaissance that impacted Shakespeare was the focus on humanism—an intellectual movement that emphasized the value of human experience and reason. Shakespeare’s works reflect this through his complex characters who grapple with questions of identity, morality, and personal choice. His characters are not just symbolic representations of good or evil; they are deeply human, with strengths, flaws, and desires that make them relatable to audiences across centuries.
Additionally, the Renaissance revival of classical Greek and Roman literature provided Shakespeare with a rich source of inspiration. He incorporated classical themes, such as fate, ambition, and tragedy, into his plays. His use of classical references and structure, while adapting them to his own style, demonstrates how the Renaissance influenced his approach to both storytelling and character development.
By drawing on Renaissance ideals, Shakespeare created works that were not only a reflection of his time but also a timeless exploration of human nature, making his plays resonate with audiences to this day.
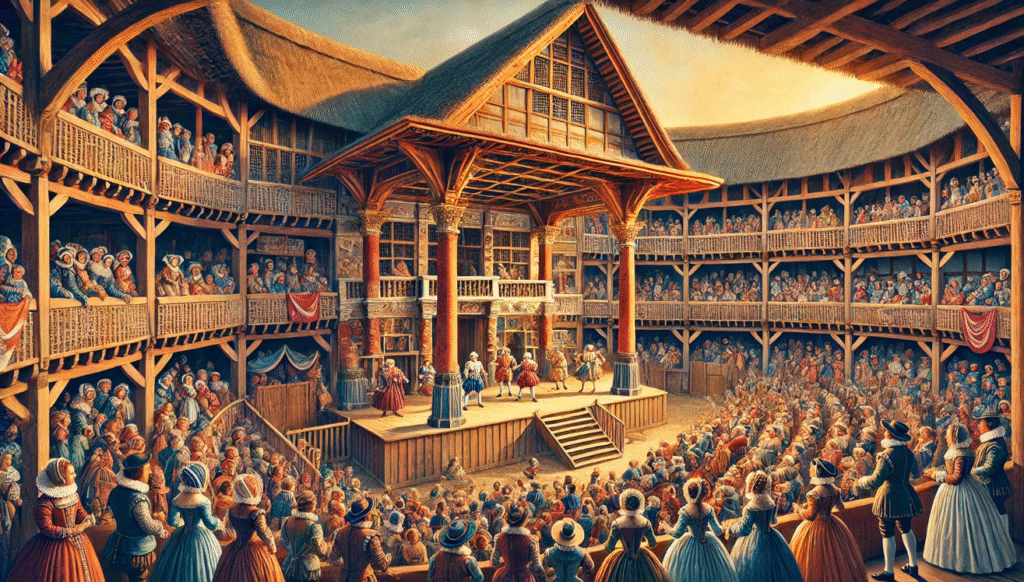
The Impact of Theater in Shakespeare’s Time

The theater was central to life in Elizabethan England, and its influence on Shakespeare’s writing cannot be overstated. During this period, public theaters like the Globe Theatre became popular gathering places for audiences of all social classes. Shakespeare’s plays were written not only to be read but to be performed, which shaped his unique writing style.
In this dynamic theater environment, Shakespeare crafted his works with an eye toward the stage. His use of vivid imagery, powerful dialogue, and distinct character voices was tailored to captivate live audiences. The need for strong, clear performances influenced his choice of language—his characters often speak directly to the audience through soliloquies or engaging dialogue, making the experience more intimate.
Additionally, the diverse audience of the time, ranging from nobility to commoners, meant that Shakespeare had to balance complex themes with accessibility. This influenced the way he blended humor, drama, and deep philosophical ideas, ensuring his plays appealed to all types of viewers. The public theater also encouraged experimentation with genre, allowing Shakespeare to seamlessly mix tragedy, comedy, and history in ways that were both entertaining and thought-provoking.
The vibrant theater scene of Shakespeare’s time not only shaped the structure and style of his plays but also ensured that his work reached a broad, dynamic audience, leaving a lasting mark on the world of drama.
Shakespeare’s Language: A Reflection of Historical Context

Shakespeare’s use of language is one of the most distinctive features of his writing and offers a direct reflection of the historical context in which he wrote. The Elizabethan era was a time of linguistic transition, as the English language was evolving from Middle English into Early Modern English. Shakespeare played a crucial role in shaping this transformation, using language in innovative ways to express complex ideas and emotions.
At the core of Shakespeare’s language is his mastery of wordplay, metaphor, and symbolism. He often coined new words and phrases, many of which are still in use today. This creative use of language was influenced by the Renaissance’s focus on linguistic development and classical learning, which encouraged writers to experiment with vocabulary and structure.
Shakespeare also employed a rich variety of poetic forms, such as blank verse and iambic pentameter, which were popular during the Renaissance. These structures allowed him to craft rhythmically beautiful and intellectually engaging dialogue. His ability to manipulate language not only enhanced the emotional depth of his characters but also made his plays more memorable and impactful.
Social and Political Influences on Shakespeare’s Themes and Style

Shakespeare’s works were deeply influenced by the social and political climate of Elizabethan England. This period was marked by political tensions, class struggles, and changing social norms—all of which shaped the themes and style of Shakespeare’s writing.
Politically, England was navigating its relationship with Catholic Europe, especially in light of the Protestant Reformation. These tensions are evident in many of Shakespeare’s plays, where themes of power, authority, and the divine right of kings are explored. For instance, in Macbeth and Richard III, the struggle for the throne and the consequences of political ambition reflect the uncertainty of the time.
Socially, Shakespeare was writing during a time of rigid class structures. However, his plays often challenge these norms. Characters from lower social classes, such as Falstaff in Henry IV and the gravedigger in Hamlet, are portrayed with complexity and wit, giving them depth that transcends their social position. Shakespeare’s ability to address issues of class and identity made his works relevant to a broad audience.
Additionally, gender roles and expectations were central to many of Shakespeare’s plays. The portrayal of women in works like Macbeth, Othello, and Twelfth Night reflects the tensions surrounding gender in Elizabethan society. Shakespeare often explored the limitations placed on women and the power dynamics in relationships, offering insight into the evolving role of women in both society and theater.
By examining these social and political influences, we gain a deeper understanding of how Shakespeare’s works were a reflection of the time in which they were written, and how they continue to resonate with audiences today.
Shakespeare’s Mastery of Dramatic Structure and Style

Shakespeare’s genius lies not only in his characters and language but also in his mastery of dramatic structure and style. His ability to blend different genres, use complex plot structures, and develop his characters through dialogue set him apart as a playwright.
One of the key elements of Shakespeare’s dramatic style is his use of soliloquies. These powerful monologues give audiences a direct window into a character’s inner thoughts and motivations. From Hamlet’s famous “To be or not to be” soliloquy to Lady Macbeth’s reflection on guilt, Shakespeare uses these moments to deepen character development and create emotional connections with the audience.
Shakespeare also excelled at blending tragedy, comedy, and history, often within a single play. For example, The Merchant of Venice mixes moments of dark tragedy with comedic relief, while The Winter’s Tale moves from a tragic loss to a redemptive conclusion. This flexibility in genre allows his works to address a wide range of human experiences and emotions, making them timeless.
Another hallmark of Shakespeare’s style is his use of dramatic irony, where the audience knows something that the characters do not. This technique, especially prominent in plays like Romeo and Juliet and King Lear, creates suspense and heightens emotional impact as audiences anticipate the inevitable consequences of characters’ actions.
By mastering these structural techniques, Shakespeare crafted plays that were not only compelling but also deeply resonant, creating a dynamic experience for both performers and audiences alike. His innovative use of dramatic form continues to influence playwrights and theater artists today.
Shakespeare’s Enduring Legacy: Why Historical Context Still Matters

Shakespeare’s works have transcended time, becoming some of the most performed and studied plays in the world. But to truly understand and appreciate his genius, it’s crucial to recognize the historical context in which he wrote. The social, political, and cultural factors of the Elizabethan era are not just background details; they are integral to the themes, characters, and storytelling techniques that make Shakespeare’s plays so powerful.
By studying the historical context, we gain insight into the motivations behind his characters and the social commentary embedded in his works. For example, Shakespeare’s exploration of power dynamics, gender roles, and class structures offers a window into the concerns of his time, many of which remain relevant today. His ability to capture the complexities of human nature through historical and social lenses allows his works to resonate with modern audiences in a way that few other playwrights can achieve.
Moreover, Shakespeare’s historical context influenced his writing style, from the language he used to the way he structured his plays. Understanding the evolution of the English language during the Renaissance, for instance, enhances our appreciation of Shakespeare’s wordplay, innovation, and ability to shape the English lexicon.
Ultimately, Shakespeare’s enduring legacy lies not only in the timelessness of his stories but also in how deeply his works are rooted in the world he lived in. Appreciating the historical forces that shaped his writing allows us to connect more deeply with his masterpieces and ensures their relevance for generations to come.
In conclusion, understanding the historical context of Shakespeare’s writing style is key to fully appreciating the depth and richness of his masterpieces. The Elizabethan era, with its political unrest, social dynamics, and cultural shifts, profoundly shaped Shakespeare’s works, from his use of language to his exploration of universal themes. By examining the influence of the Renaissance, the impact of theater, and the social and political landscape of his time, we can better understand how Shakespeare crafted his timeless characters and compelling narratives.
Shakespeare’s ability to weave together historical, social, and personal elements in his plays not only reflects the world he inhabited but also connects with audiences across centuries. His mastery of dramatic structure, poetic language, and complex character development ensures that his work remains relevant and impactful today. By recognizing the historical context in which Shakespeare wrote, we can gain a deeper understanding of why his works continue to resonate, offering timeless insights into the human condition.