The impact of Shakespeare on literary movements works have echoed through centuries, influencing not only the evolution of literature but also the way we understand the human condition. From his intricate characterizations to his profound explorations of power, love, and ambition, Shakespeare’s influence continues to shape the literary landscape. The impact of Shakespeare on literary movements one fascinating aspect of this legacy is how his impact transcended his time, touching upon various literary movements, from the Renaissance to Modernism, and still reverberates today. This article delves into the impact of Shakespeare on literary movements, exploring how his works have profoundly shaped modern literature and continue to inspire writers across generations. Through this analysis, we will uncover the lasting power of his words and their ability to mold the direction of literary traditions, both past and present.
The impact of Shakespeare on literary movements works have echoed through centuries, influencing not only the evolution of literature but also the way we understand the human condition. From his intricate characterizations to his profound explorations of power, love, and ambition, Shakespeare’s influence continues to shape the literary landscape. The impact of Shakespeare on literary movements one fascinating aspect of this legacy is how his impact transcended his time, touching upon various literary movements, from the Renaissance to Modernism, and still reverberates today. This article delves into the impact of Shakespeare on literary movements, exploring how his works have profoundly shaped modern literature and continue to inspire writers across generations. Through this analysis, we will uncover the lasting power of his words and their ability to mold the direction of literary traditions, both past and present.
Shakespeare’s Influence on the Renaissance

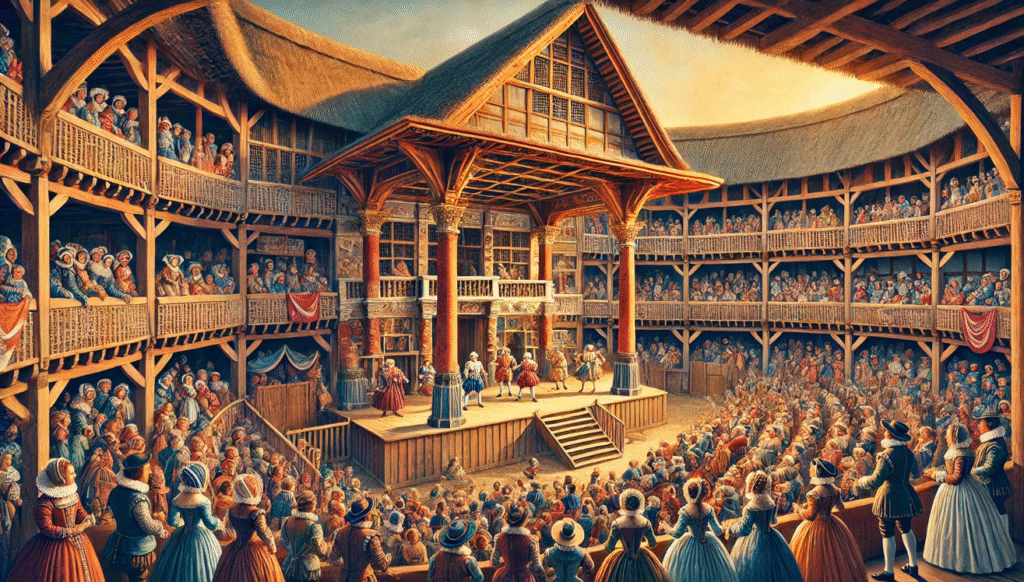
The impact of Shakespeare on literary movements was a period of intellectual and artistic rebirth, and Shakespeare’s contributions were pivotal in the flourishing of English literature during this time. The impact of Shakespeare on literary movements works not only reflected the era’s fascination with humanism and the exploration of individual potential but also shaped the direction of English drama.
Shakespeare’s ability to blend classical influences with his unique voice led to the development of a new kind of theater—one that combined complex characters, rich dialogue, and intricate plots. His plays, such as Hamlet and A Midsummer Night’s Dream, resonated with the Renaissance ideals of intellectual exploration, the complexities of human nature, and the importance of individual experience.
Through his vivid characters and their emotional depth, Shakespeare helped elevate drama to a form of high art. He influenced other playwrights, including Christopher Marlowe and Ben Jonson, who also embraced the Renaissance focus on human potential and the complexities of the human soul.
Shakespeare’s lasting impact on the Renaissance demonstrates his ability to merge intellectual ideas with entertainment, creating works that continue to influence writers and playwrights across centuries.
Shakespeare and the Enlightenment
The Enlightenment, a period focused on reason, individual rights, and the questioning of traditional authority, found resonance in Shakespeare’s works. His deep exploration of human nature, morality, and political power provided fertile ground for Enlightenment thinkers and playwrights who sought to challenge societal norms.
Shakespeare’s plays, particularly King Lear and Macbeth, tackled themes of authority, justice, and the human condition—issues central to Enlightenment thought. His portrayal of rulers who grapple with power and moral dilemmas mirrored the Enlightenment’s skepticism of absolute authority and its emphasis on reasoned governance.
Moreover, Enlightenment writers like Voltaire and Jean-Jacques Rousseau admired Shakespeare’s ability to expose the flaws of human nature and the complexities of personal choice. His work inspired a more critical, intellectual approach to theater, influencing the rise of tragedy as a vehicle for philosophical exploration.
Shakespeare’s nuanced character studies, especially his psychological depth, gave voice to Enlightenment values of individualism and personal responsibility, making his work an enduring part of intellectual discourse during this transformative period.
The Impact on Romanticism

The Romantic movement, with its emphasis on emotion, individualism, and the sublime, found a deep connection with Shakespeare’s works. Romantic writers, poets, and playwrights admired Shakespeare’s ability to explore raw human emotions and the complexities of individual experience.
Shakespeare’s characters, often torn between love, ambition, and moral conflict, mirrored the Romantics’ interest in inner turmoil and personal freedom. His plays, such as Romeo and Juliet and The Tempest, captured the intense emotions and the struggle for personal expression that were central to Romantic ideals.
Writers like Lord Byron, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, and Percy Bysshe Shelley were particularly influenced by Shakespeare’s vivid portrayals of emotion and the supernatural. They drew inspiration from his exploration of the human psyche and his ability to portray profound inner conflicts, shaping their own works with similar themes of individual struggle and emotional intensity.
Shakespeare’s impact on Romanticism helped elevate literature beyond reason and logic, championing the expressive power of the human heart and mind—a hallmark of the movement. His legacy continues to resonate in modern literature, where his themes of passion and personal freedom remain timeless.
Shakespeare’s Influence on Victorian Literature
The Victorian era, marked by its focus on morality, social responsibility, and the complexities of human character, was deeply influenced by Shakespeare’s works. His ability to explore the human condition in all its depth and complexity resonated with Victorian writers who sought to portray both the virtues and flaws of society.
Shakespeare’s plays, particularly Hamlet and Othello, offered rich psychological insight into characters wrestling with moral dilemmas, identity, and societal expectations. These themes paralleled the Victorians’ concerns with personal integrity, social progress, and the tension between tradition and change.
Victorian writers such as Charles Dickens, George Eliot, and Thomas Hardy found inspiration in Shakespeare’s portrayal of social structures, personal conflict, and the consequences of human actions. His exploration of class, ambition, and justice influenced the way Victorian authors addressed these issues in their own works, particularly in the evolving social landscape of the time.
Shakespeare’s impact on Victorian literature helped elevate drama and storytelling as tools for social reflection and moral inquiry, making his influence enduring in both literary tradition and the broader cultural discourse of the era.
Shakespeare’s Influence on Modernist Literature

Modernism, known for its break with tradition and experimentation with form and narrative, was profoundly shaped by Shakespeare’s works. Modernist writers, seeking to explore the complexities of the human psyche and society, found in Shakespeare’s plays a rich source of inspiration.
Shakespeare’s plays, especially Hamlet, Macbeth, and The Tempest, are known for their intricate character studies and exploration of existential themes—topics that aligned perfectly with Modernist concerns. Writers like T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, and Virginia Woolf drew from Shakespeare’s ability to portray fragmented identities, internal conflicts, and the complexity of human emotions, using similar techniques in their own works.
Shakespeare’s experimental use of language and structure also influenced Modernist writers, who pushed the boundaries of narrative form. Just as Shakespeare manipulated traditional theatrical structures, Modernists challenged linear storytelling, playing with time, perspective, and language to create new ways of representing reality.
By drawing on Shakespeare’s psychological depth and narrative innovation, Modernist writers advanced the exploration of human consciousness and broke away from conventional storytelling, helping shape modern literature as we know it today.
Shakespeare’s Impact on Contemporary Literature
Shakespeare’s influence on contemporary literature remains profound, with his themes, characters, and storytelling techniques continuing to shape modern writers and their works. His exploration of universal human experiences—love, betrayal, power, and identity—resonates deeply with today’s readers, making his works timeless.
Contemporary authors often draw inspiration from Shakespeare’s complex characters and intricate plots. Many modern novels, plays, and films directly adapt his stories, reimagining classics like Macbeth, Romeo and Juliet, and Hamlet for new audiences. These adaptations maintain the emotional depth and moral conflicts of the original works while updating them for contemporary settings.
In addition to direct adaptations, Shakespeare’s influence can be seen in the way modern authors address themes of personal struggle and societal issues. Writers like Toni Morrison, Margaret Atwood, and Tom Stoppard use Shakespearean elements to explore complex human emotions, power dynamics, and the consequences of individual choices.
Shakespeare’s impact on contemporary literature proves that his works continue to inspire and challenge writers to engage with the core of the human experience, ensuring that his legacy remains central to modern storytelling.
Shakespeare’s influence on literature has transcended time and continues to shape the way we understand and engage with stories. From the Renaissance to modern times, his ability to delve into the complexities of human nature, explore moral dilemmas, and create unforgettable characters has left an indelible mark on literary movements across centuries. Whether through his impact on the Renaissance’s intellectual landscape, his influence on the emotional intensity of Romanticism, or his ability to inspire contemporary writers, Shakespeare’s works remain an enduring source of inspiration.
As we continue to adapt, reinterpret, and learn from Shakespeare’s timeless themes, his influence on modern literature remains undeniable. His legacy is not just in the pages of his plays but in the way writers today continue to explore the depths of the human experience. Shakespeare’s works are not merely historical artifacts—they are living, breathing pieces of art that still speak to the challenges, passions, and complexities of our world. His impact on literary movements proves that the power of storytelling knows no bounds and that the lessons from his work will resonate for generations to come.