Elizabethan societal changes and Shakespeare which lasted from 1558 to 1603, was a time of significant societal and cultural transformations in England. It was a period marked by the flourishing of the arts, literature, and exploration, as well as the establishment of the Church of England and the rise of the British Empire. During this time, there was a growing interest in literature and the arts, and the popularity of theater thrived. Elizabethan societal changes and Shakespeare it was also a time of great political and religious upheaval, with the reign of Queen Elizabeth I and the tensions between Catholics and Protestants. William Shakespeare emerged as a pivotal figure in Elizabethan literature, producing some of the most enduring and influential works in the English language.
Elizabethan societal changes and Shakespeare which lasted from 1558 to 1603, was a time of significant societal and cultural transformations in England. It was a period marked by the flourishing of the arts, literature, and exploration, as well as the establishment of the Church of England and the rise of the British Empire. During this time, there was a growing interest in literature and the arts, and the popularity of theater thrived. Elizabethan societal changes and Shakespeare it was also a time of great political and religious upheaval, with the reign of Queen Elizabeth I and the tensions between Catholics and Protestants. William Shakespeare emerged as a pivotal figure in Elizabethan literature, producing some of the most enduring and influential works in the English language.
Overview of Elizabethan Societal Changes
The Rise of the Renaissance in England
The European Renaissance had a profound influence on arts, culture, and intellectual pursuits. Elizabethan societal changes and Shakespeare it sparked a renewed interest in the classical learning of ancient Greece and Rome, leading to a revival of literature, art, and philosophy. One of the key developments of the Renaissance was the rise of humanism, which emphasized the importance of human potential and achievement. Elizabethan societal changes and Shakespeare this shift in thinking had a significant impact on literary themes, as writers began to focus on the individual and human experience. Humanist ideas also inspired a greater emphasis on the use of vernacular languages in literature, allowing for a wider audience to engage with literary works.
Religious Turmoil and the Reformation

The Protestant Reformation was a significant movement in the 16th century that challenged the authority of the Catholic Church and led to the creation of Protestant denominations. This tension between Catholicism and Protestantism greatly impacted societal values, as it sparked debates and disagreements on religious beliefs and practices. The Reformation brought about changes in the way people viewed spirituality and the role of the church in their lives. It led to the rise of individual interpretation of scripture and a focus on personal faith, which in turn influenced daily life and societal values. The Reformation also played a role in shaping political and social structures, as rulers and governments aligned themselves with either Catholicism or Protestantism, leading to conflicts and wars in some regions.
Social Hierarchy and Class Dynamics

The rigid class system of Elizabethan society was structured with clear distinctions between monarchs, nobility, gentry, and commoners. However, increased mobility within social classes began to occur due to the rise of commerce and exploration during this time period. In Shakespeare’s plays, such as Romeo and Juliet and Hamlet, we can see reflections of the social class system through the interactions and conflicts between characters from different backgrounds. These works often explore the complexities and tensions that arise from the rigid class structure, providing insight into the social dynamics of Elizabethan society.
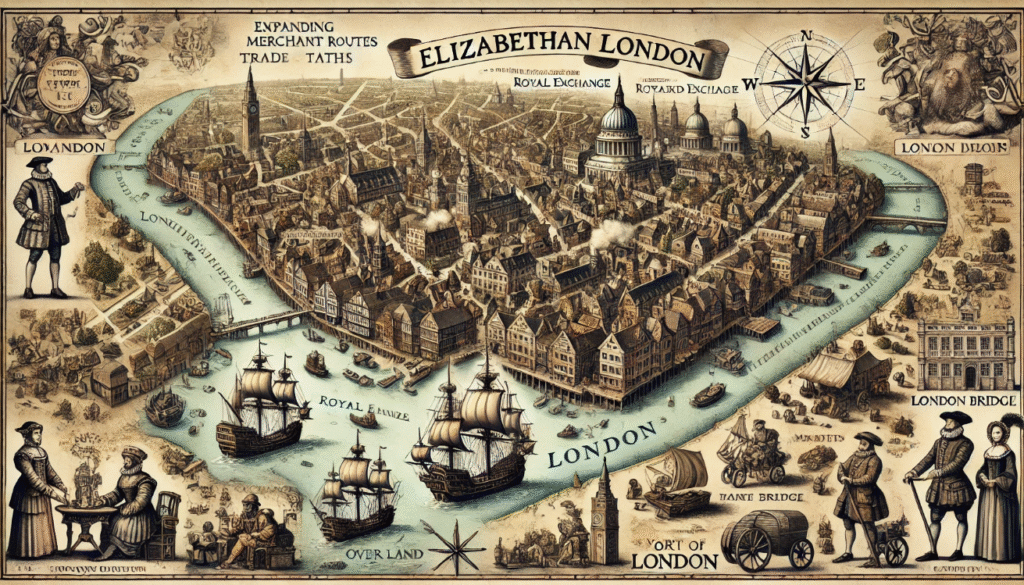
The Impact of Exploration and Global Expansion

The rise of England as a maritime power and the beginnings of global trade were significant factors that contributed to the country’s economic and political growth. This expansion of trade routes allowed for the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences from around the world. As a result, new ideas and cultural influences were brought to England, which were reflected in its literature. This period of global trade and exploration had a profound impact on England’s development and helped shape its identity as a major player in international affairs.
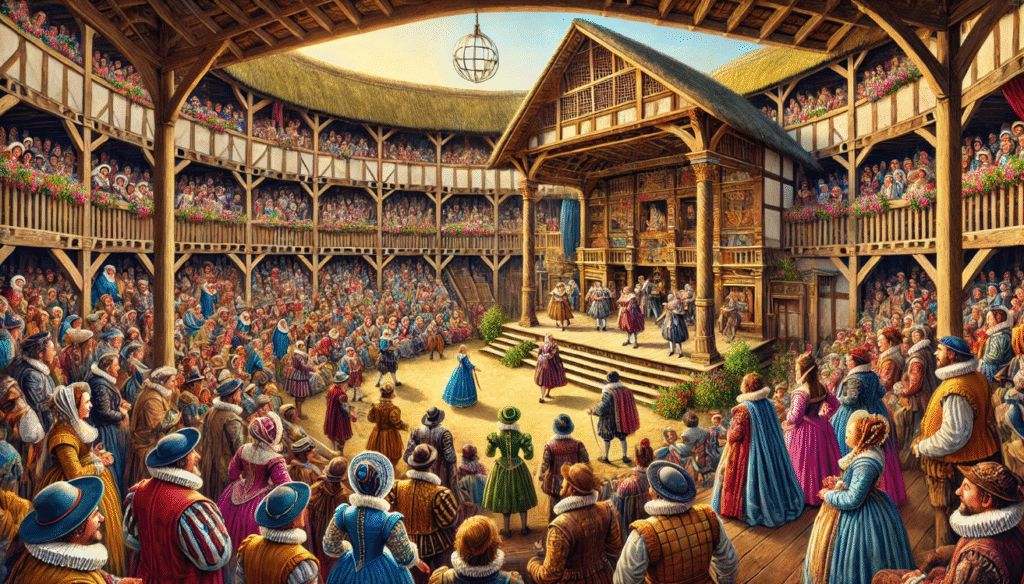
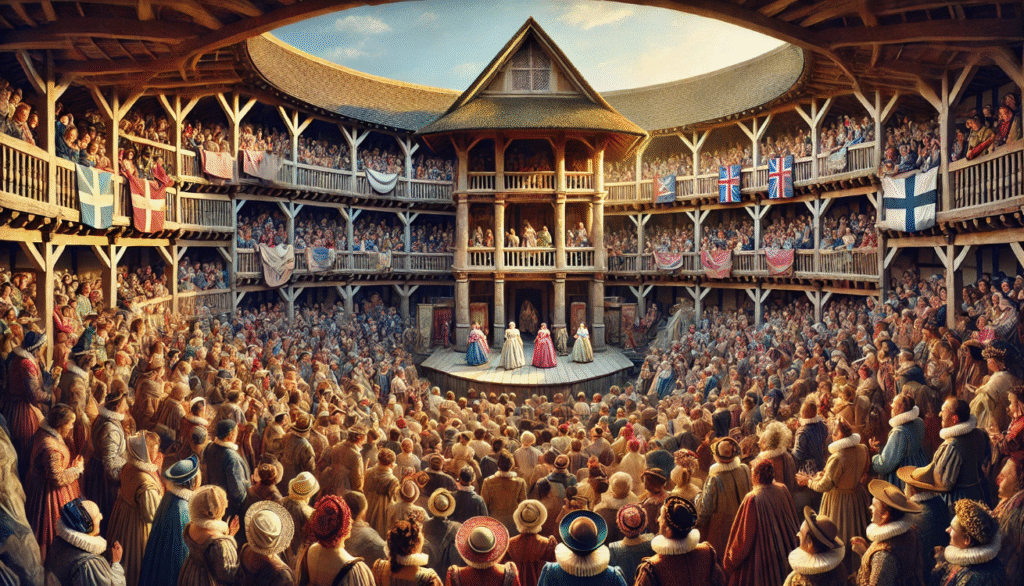
The Role of Theater in Elizabethan Society

The Globe Theatre was a central hub for entertainment and public discourse during the Renaissance era in England. It was a popular gathering place for people of all social classes, who came to watch plays, hear music, and engage in lively discussions. The plays performed at the Globe often reflected and shaped public opinion, making it an important venue for cultural and political expression. The theater’s popularity and influence played a significant role in shaping the social and intellectual landscape of the time.
Shakespeare’s Adaptation to Elizabethan Changes

Integration of Humanist Ideals
The integration of humanist ideals in Shakespeare’s plays is evident through the exploration of universal human experiences, morality, and individuality in works like Hamlet and Macbeth. These plays reflect the Renaissance philosophy of the time through their characters and themes. b) Shakespeare’s works also contain subtle commentary on religious tensions, as seen in plays such as Measure for Measure and King Lear. Additionally, political themes in his plays mirror the concerns of Elizabethan society, as evidenced in works like Julius Caesar.
Representation of Social Hierarchies
Shakespeare challenged class boundaries in his plays by using commoners as central characters, such as Bottom in A Midsummer Night’s Dream. This allowed him to explore the lives and perspectives of those outside the upper class, giving a more nuanced portrayal of different social strata. Additionally, Shakespeare reflected global expansion in his plays through themes of exploration and cultural encounters, particularly in works like The Tempest and Othello. His nuanced portrayal of foreigners and “the other” allowed him to depict the complexities of cross-cultural interactions and the impact of global expansion on society. These elements added depth and richness to his exploration of class boundaries and societal dynamics.
Key Works Highlighting Elizabethan Societal Changes

Romeo and Juliet

Hamlet is a complex and thought-provoking play that delves into the clash of familial loyalty versus individual love amidst social constraints. The play also serves as a reflection of social tensions and intergenerational conflicts, as well as a philosophical exploration of morality, revenge, and human nature influenced by Renaissance ideals. Additionally, it sheds light on political instability and questions of succession, making it a rich and multifaceted work that continues to resonate with audiences today.
The Merchant of Venice
In “The Tempest,” Shakespeare explores the themes of colonialism and the power dynamics between the colonizer and the colonized. The play offers a commentary on the expansion of England’s global influence during the Elizabethan era. Through the character of Prospero and his interactions with Caliban and Ariel, the play delves into issues of control, exploitation, and the impact of colonization on indigenous peoples. Shakespeare’s examination of these themes sheds light on the complexities of colonialism and its effects on both the colonizer and the colonized.
Shakespeare’s Legacy as a Product of His Time

Shakespeare’s works serve as a valuable historical record of Elizabethan societal norms and transformations because they reflect the values, beliefs, and social structures of his time. Through his plays and poems, he captured the essence of Elizabethan society, including its class divisions, gender roles, political tensions, and cultural dynamics. His ability to transcend time by addressing universal themes rooted in his contemporary context allows modern audiences to connect with his works on a deeply personal level. Despite being deeply tied to Elizabethan changes, his exploration of themes such as love, power, ambition, and human nature continue to resonate with modern audiences, making his works timeless and relevant to this day.
Modern Relevance of Shakespeare’s Reflection on Elizabethan Society

Shakespeare’s exploration of societal change in his works remains relevant today as it provides valuable lessons on adapting to shifts and challenges within our own society. His plays often depict the consequences of societal upheaval and the need for individuals to navigate and respond to these changes. By examining characters who grapple with issues such as power struggles, cultural shifts, and changing social norms, we can gain insight into how to address similar issues in our own time. Shakespeare’s timeless themes of societal change offer valuable perspectives on how to navigate and adapt to the ever-evolving world around us.
During the Elizabethan era, England experienced significant societal changes that greatly influenced the work of William Shakespeare. These changes included the rise of the merchant class, exploration and expansion of trade, and the emergence of new scientific and philosophical ideas. As a playwright, Shakespeare was able to tap into these changes and use them as inspiration for his timeless works. He captured the essence of his time while addressing universal human concerns such as love, jealousy, power, and the complexities of the human experience. Shakespeare’s genius lies in his ability to not only reflect the society he lived in but also to transcend it by delving into the depths of human emotions and experiences. His plays continue to resonate with audiences across generations because they speak to universal truths about the human condition.