William Shakespeare is widely regarded as the greatest playwright in history, and his works have had a profound impact on literature and drama. History of Shakespearean plays, such as Hamlet, Macbeth, and Romeo and Juliet, have had a lasting influence on storytelling and continue to be performed and studied around the world. In this article, we will explore the history of Shakespeare and his works, the impact his plays have had on literature and drama, and his enduring legacy in the world of theater. We will delve into the timeless themes and characters in his plays, and examine how his work continues to resonate with audiences centuries after they were written. Join us as we celebrate the legacy history of Shakespearean plays, the master of the stage.
William Shakespeare is widely regarded as the greatest playwright in history, and his works have had a profound impact on literature and drama. History of Shakespearean plays, such as Hamlet, Macbeth, and Romeo and Juliet, have had a lasting influence on storytelling and continue to be performed and studied around the world. In this article, we will explore the history of Shakespeare and his works, the impact his plays have had on literature and drama, and his enduring legacy in the world of theater. We will delve into the timeless themes and characters in his plays, and examine how his work continues to resonate with audiences centuries after they were written. Join us as we celebrate the legacy history of Shakespearean plays, the master of the stage.
The Early Years of Shakespearean Theatre

William Shakespeare was born in 1564 in Stratford-upon-Avon, a bustling market town in England. He was the third of eight children and his father, John Shakespeare, was a prominent local figure. Shakespeare’s early life in Stratford-upon-Avon exposed him to the world of drama and literature. His education at the King Edward VI Grammar School provided him with a strong foundation in Latin and classical literature, which would later influence his writing. The rise of Renaissance theatre in England during history of Shakespearean plays early years was a significant factor in shaping his career. The flourishing of the arts and the patronage of Queen Elizabeth I and King James I provided opportunities for playwrights like Shakespeare to thrive.
The Golden Age of Shakespearean Plays (1590-1610)

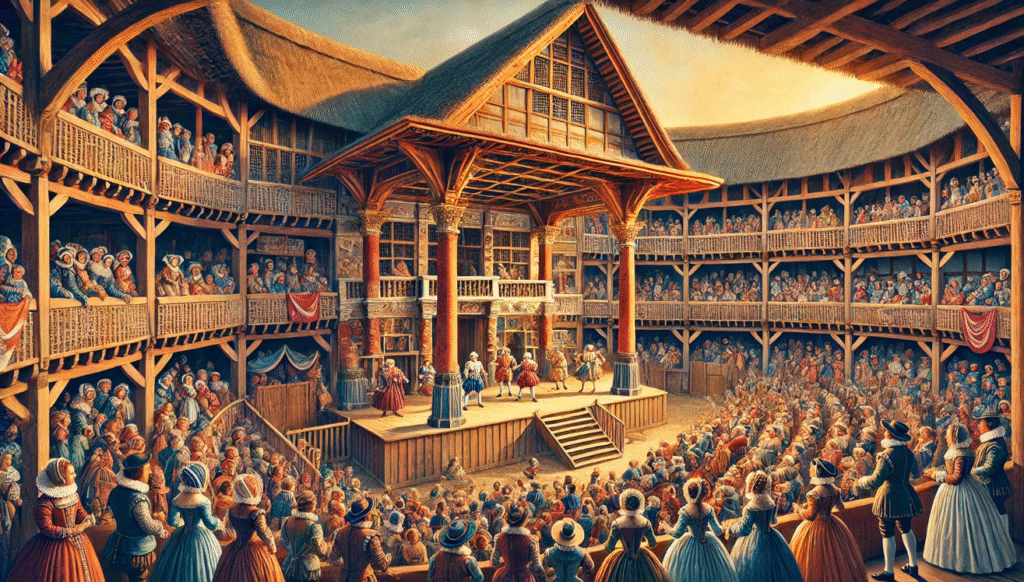
History of Shakespearean plays was closely associated with The Lord Chamberlain’s Men, a leading theatrical company in London, and later The King’s Men, which was the official royal company. The Globe Theatre, where many of his plays were performed, played a significant role in popularizing his works and attracting large audiences. Some of Shakespeare’s early successes included the Henry VI trilogy, Richard III, and Titus Andronicus. These plays helped establish his reputation as a playwright. Shakespeare’s major tragedies and comedies, such as Hamlet, Othello, Macbeth, A Midsummer Night’s Dream, and Twelfth Night, are still widely performed and studied today. Queen Elizabeth I and King James I both had a significant influence on Shakespearean theatre.
Themes and Styles in Shakespearean Plays

Tragedies such as Hamlet, King Lear, and Macbeth often explore themes of fate, ambition, revenge, and morality. These plays delve into the darker aspects of human nature and often end with the downfall of the main characters. On the other hand, comedies like Much Ado About Nothing and As You Like It tend to focus on themes of love, mistaken identities, humor, and ultimately conclude with a happy ending. These plays are known for their lighthearted and enjoyable tone, providing entertainment and a sense of joy for the audience.
The histories, such as Henry V and Richard III, are important depictions of English kings and their impact on national identity. These plays often explore themes of power, leadership, and the consequences of their actions. On the other hand, the late romances, like The Tempest and The Winter’s Tale, blend elements of tragedy and comedy. These plays often feature magical elements and explore themes of forgiveness, reconciliation, and redemption. Shakespeare’s writing style in these plays often includes the use of blank verse, soliloquies, and iambic pentameter. These literary devices help to create rhythm and dramatic tension, adding depth and complexity to the characters and their experiences.
The Decline and Shakespeare’s Final Years (1610-1616)

The shift in Shakespeare’s writing from tragedy to romance marked a significant evolution in his storytelling style. During this period, he explored themes of reconciliation, forgiveness, and the power of love. It’s believed that this change may have been influenced by personal experiences and a shift in his outlook on life. After a successful career in London, Shakespeare retired to his hometown of Stratford-upon-Avon. This allowed him to spend more time with his family and focus on his personal interests. It’s also during this time that he may have written his last works, including The Tempest, Henry VIII, and The Two Noble Kinsmen. Shakespeare’s death in 1616 was a great loss to the literary world.
The Posthumous Influence of Shakespearean Plays

The First Folio, published in 1623, played a crucial role in preserving the works of William Shakespeare. It was the first collected edition of his plays and is credited with preserving 36 of his plays, 18 of which had not been previously published. This collection has been instrumental in shaping our understanding of Shakespeare’s work and has had a lasting impact on the preservation of his plays. In the 18th and 19th centuries, there was a significant revival of Shakespearean drama. This period saw a renewed interest in his works, leading to numerous adaptations, performances, and scholarly studies. This revival helped to solidify Shakespeare’s place as one of the most important and influential playwrights in history.
The impact of modern literature, film, and pop culture on each other has been profound. Many popular books have been adapted into blockbuster Hollywood films, reaching a global audience and influencing popular culture around the world. These adaptations often bring new life to beloved stories, introducing them to new generations and sparking renewed interest in the source material. Additionally, global performances of these adaptations, such as stage plays and musicals, further extend their reach and impact. As a result, modern literature, film, and pop culture continue to intersect and influence each other, shaping the way we experience and engage with stories in the 21st century.

Shakespeare’s plays continue to be studied and performed worldwide due to their enduring relevance, universal themes, and timeless characters. His works explore the complexities of the human experience, and their profound insight into human nature and emotions resonates with audiences across cultures and time periods. Additionally, the beauty and richness of Shakespeare’s language and the depth of his storytelling continue to captivate and inspire actors, directors, and scholars around the globe. As a result, his plays remain an integral part of the theatrical canon and are continuously celebrated and interpreted in diverse and innovative ways.
Shakespearean plays hold significant historical importance as they revolutionized the English language and storytelling. His works have had a lasting influence on drama, language, and storytelling, setting the standard for literary excellence. Shakespeare’s ability to capture the depth of human emotion and explore timeless themes such as love, power, and ambition has made his works relevant in the modern era. His plays continue to be studied, performed, and adapted, demonstrating their enduring impact on literature and culture.