The Elizabethan Era, which lasted from 1558 to 1603, was a period of political stability under the rule of Queen Elizabeth I. This era also saw the rise of the Renaissance, a time of great intellectual and artistic growth, as well as the flourishing of English culture. It was a time of exploration, expansion, and innovation, and it left a lasting impact on the arts, literature, and politics.
The Elizabethan Era, which lasted from 1558 to 1603, was a period of political stability under the rule of Queen Elizabeth I. This era also saw the rise of the Renaissance, a time of great intellectual and artistic growth, as well as the flourishing of English culture. It was a time of exploration, expansion, and innovation, and it left a lasting impact on the arts, literature, and politics.
Theatre has played a significant role as a key form of Shakespeare’s portrayal of Elizabethan society entertainment and social commentary throughout history, particularly in societies with a structured hierarchy such as a monarchy, nobility, gentry, and commoners. It has served as a platform for reflecting and critiquing the societal norms and values of the time, often providing a voice for the marginalized and oppressed. In the context of a monarchy, theatre has been used to either glorify or criticize the ruling monarch and the aristocracy. It has provided a means for exploring power dynamics, social inequality, and the struggles of the common people. Through the portrayal of different social classes and their interactions, theatre has helped to shed light on the disparities and injustices within society.
Political Commentary in Shakespeare’s Plays

Shakespeare’s exploration of power, authority, and governance is a central theme in many of his plays. In “Macbeth,” he delves into the dangers of unchecked ambition and the consequences of tyranny. The protagonist’s thirst for power leads to his downfall, highlighting the destructive nature of absolute authority. In “Julius Caesar,” Shakespeare examines the complexities of political manipulation and betrayal, showcasing the fragility of leadership and the impact of disloyalty on governance. Through these works, Shakespeare offers a thought-provoking commentary on the intricacies of power and the ramifications of its abuse.
During the Elizabethan era, England experienced significant political anxieties surrounding succession issues, fear of rebellion, and the concept of the divine right of kings. The lack of a clear heir to the throne and the potential for power struggles created uncertainty and unease among the ruling class and the general population. Moreover, the fear of rebellion, particularly from Catholic factions and rival claimants to the throne, added to the overall sense of instability. Additionally, the belief in the divine right of kings, which asserted that monarchs were chosen by God and therefore had absolute authority, created tension and uncertainty about the legitimacy of the ruling monarch.
Shakespeare’s works often contain subtle critiques of authority, whether it be the monarchy, church, or other forms of power. He navigated censorship by using clever language and ambiguous themes to convey his criticisms without directly challenging those in power. His ability to navigate these restrictions allowed his works to be performed and appreciated, while still addressing important societal issues.
Gender Roles and Expectations in Elizabethan Society
Exploration of Shakespeare’s portrayal of women and gender roles:

Shakespeare’s portrayal of Juliet in “Romeo and Juliet” challenges traditional gender roles by depicting her as a strong and independent young woman. Despite the societal expectations placed upon her, Juliet defies her family’s wishes and pursues her own desires, ultimately choosing love over duty. This portrayal not only subverts traditional gender expectations but also highlights the agency and autonomy of women in Shakespeare’s work.
“The Taming of the Shrew” is a play written by William Shakespeare that has sparked much debate over its portrayal of patriarchal values and gender dynamics. The play follows the story of a headstrong woman named Katherina who is “tamed” by her husband Petruchio, leading to discussions about the treatment of women and power dynamics in relationships. This debate has continued for centuries and has led to various interpretations and adaptations of the play.
Representation of women in Elizabethan society:
Shakespeare’s female characters often played limited roles in society, but they also showcased evolving perspectives on gender and societal norms. They were a mix of conformity and rebellion, reflecting the tensions and complexities of the time. Shakespeare’s portrayal of women in his plays continues to be studied and debated, offering valuable insights into the historical and cultural context of his works.
Religion and Morality in Shakespeare’s Works

The Protestant Reformation had a significant impact on the religious landscape of Europe during the 16th century. It led to the breakaway of several Christian denominations from the Roman Catholic Church, resulting in religious tensions and conflicts across the continent. The Reformation also played a role in shaping the political and social dynamics of the time, as rulers and nations aligned themselves with either the Catholic or Protestant faith. These religious tensions ultimately contributed to a series of wars and conflicts, such as the Thirty Years’ War, which had a lasting impact on Europe. Overall, the Protestant Reformation and the religious tensions of the time had far-reaching consequences for the history of Europe.
Shakespeare addresses moral dilemmas and religious themes in his plays through the exploration of complex and thought-provoking issues. In “Hamlet,” the protagonist grapples with questions of morality, sin, and the afterlife, while in “Measure for Measure,” the play delves into the themes of justice, virtue, and corruption. Through these works, Shakespeare prompts audiences to consider the ethical and spiritual implications of human behavior and decision-making.
Shakespeare’s subtle handling of religious debates in his works reflects his desire to avoid controversy. Instead of directly addressing religious issues, he often used allegory, symbolism, and ambiguous language to explore complex moral and ethical questions without taking a definitive stance. This allowed him to navigate the religious tensions of his time while still engaging with important themes and ideas. Overall, Shakespeare’s approach to religious debates in his plays demonstrates his skillful ability to navigate sensitive topics with nuance and artistry.
Social Hierarchy and Class Dynamics

Reflection of class structures in Shakespeare’s plays:
Sure! “King Lear” is a play that explores the dynamics of power and the struggles of the lower classes within society. It examines the consequences of power struggles and the impact on those who are marginalized. “Twelfth Night” on the other hand, delves into the fluidity of social roles and identity, showcasing how individuals can navigate and challenge societal expectations. Both plays offer rich insights into the complexities of human relationships and societal structures.In many of Shakespeare’s plays, there is a depiction of commoners interacting with nobility. Shakespeare often explores the human universality across classes, showing the similarities and differences in how people from different backgrounds interact with one another. Commoners are often portrayed as having a deep understanding of human nature and the struggles of everyday life, while nobility is shown to have power and privilege. The interactions between these two classes often highlight themes of social hierarchy, power dynamics, and the complexities of human relationships. Shakespeare’s exploration of these dynamics adds depth and complexity to his plays, making them resonate with audiences across time and cultures.
Theatrical Practices and Audience Perspectives

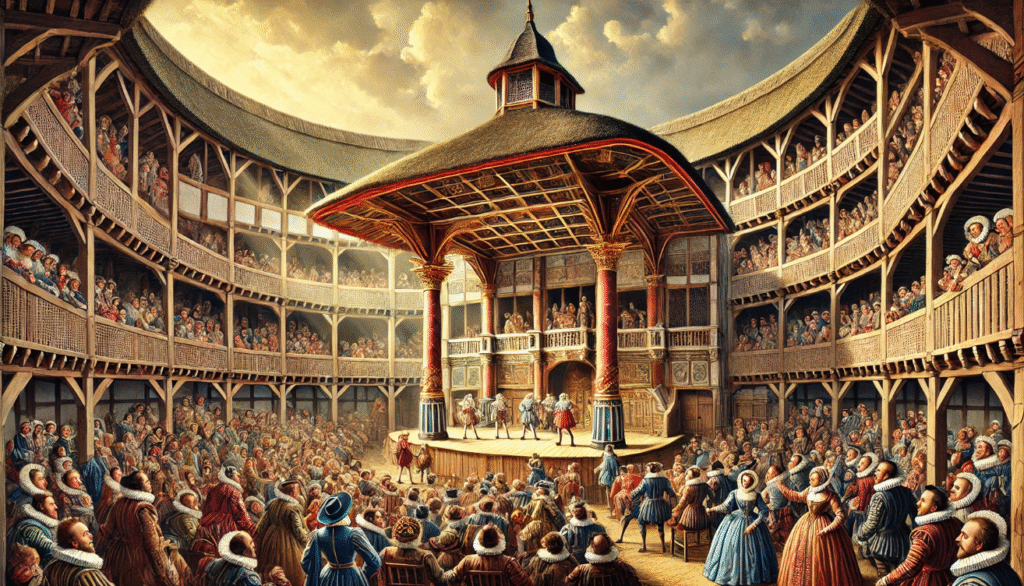
The Globe Theatre was an iconic venue for Shakespearean performances, attracting a diverse audience ranging from nobles to commoners. Shakespeare was able to cater to and reflect the interests of his audience by employing a variety of techniques. He utilized humor to entertain the lower class, while also incorporating tragic elements to appeal to the nobility. Additionally, Shakespeare often incorporated historical allegory, allowing different societal groups to find relevance and enjoyment in his works. This inclusive approach allowed the Globe Theatre to become a place where people from all walks of life could come together and appreciate the art of Shakespeare.
Timelessness of Shakespeare’s Social Commentary

Shakespeare’s portrayal of Elizabethan society resonates today because it explores universal themes such as power, identity, morality, and social order. These themes are still relevant in modern society, and Shakespeare’s exploration of them in his plays allows for a better understanding of human nature and societal dynamics. Additionally, the issues of political power, gender roles, and class distinctions that Shakespeare depicted in his works are still present in today’s world, making his portrayal of Elizabethan society still relevant and thought-provoking.
Studying Shakespeare’s works provides valuable insights into historical and contemporary societies because his plays and poetry often reflect the social, political, and cultural issues of his time. By analyzing his works, we can gain a deeper understanding of the attitudes, beliefs, and values of different historical periods, as well as how they continue to influence contemporary society. Additionally, Shakespeare’s exploration of universal themes such as love, power, and morality allows us to draw parallels between his time and our own, shedding light on the enduring relevance of his work. Overall, studying Shakespeare provides a rich and complex view of human society and its evolution over time.
Shakespeare’s works serve as a fascinating reflection of the complexities of Elizabethan society. Through his plays, he delves into the political turmoil, social hierarchies, and cultural norms of the time, providing a window into the dynamics of the era. These works are not only historical artifacts, but also timeless literature that continues to resonate with audiences today. Shakespeare’s enduring influence lies in his deep understanding of human nature and societal structures. His exploration of themes such as power, love, and ambition offers insights into the universal truths of the human experience. As a result, his works remain essential in our efforts to comprehend the intricacies of human behavior and societal dynamics.