Shakespeare’s Contribution to the Development of Theatre Arts: How His Innovations Shaped Modern Performance
Did you know that the way we experience theatre today owes much of its evolution to a playwright from the 16th century? William Shakespeare, often hailed as one of the greatest literary figures in history, was not only a master of words but also a revolutionary force in the development of theatre arts. His groundbreaking innovations transformed every aspect of the stage—from how stories were told to how actors performed. But what exactly were Shakespeare’s contributions to the development of theatre arts, and why are they still so crucial in shaping modern performance?
In this article, we’ll explore how Shakespeare’s creative genius redefined the theatre landscape and continue to influence the craft even today. Whether you’re a theatre enthusiast, aspiring actor, or simply curious about the origins of modern performance, you’ll discover how Shakespeare’s unique contributions continue to shape the way stories are told on stage. Ready to dive in? Let’s uncover the genius behind the man who changed theatre forever!
Table of Contents
Toggle1: The Early Foundations of Shakespearean Theatre 🎭
Before Shakespeare’s time, English theatre was relatively simple and often relied on morality plays, where good and evil characters taught moral lessons. These plays were performed in town squares and inns, with minimal staging and very basic scripts. The focus was more on religious themes and less on deep, complex storytelling.
Shakespeare entered this landscape during the Elizabethan era (1558–1603), a time when the arts were flourishing, but the theatre still lacked the depth and sophistication we see today. His genius didn’t just lie in writing plays, but in his ability to reshape the very structure of the stage and performance. So, what did Shakespeare bring to the table?
1.1 The Rise of Professional Theatre Companies
Before Shakespeare, theatre was mostly a side hustle for traveling performers or amateur actors. However, Shakespeare was part of a shift that made theatre a legitimate profession. He became a shareholder in the famous acting troupe, the Lord Chamberlain’s Men, which later became the King’s Men. This move was crucial in raising the status of theatre as a respected profession.
1.2 The Birth of Public Theatres
Shakespeare’s impact extended to the physical space of the theatre as well. Before the large public theatres of his time, performances were often held in small, private settings. Shakespeare’s plays were performed at The Globe Theatre, a revolutionary venue that allowed thousands of spectators to watch plays. The open-roofed design and thrust stage were designed to make the audience feel close to the action, creating an immersive experience that many modern theatres still use today.
1.3 The Introduction of Complex Plotlines and Themes
Unlike earlier plays that were simple moral tales or comedies, Shakespeare’s works introduced multifaceted plots with rich themes like betrayal, love, revenge, and political intrigue. Plays like “Hamlet” and “Macbeth” were groundbreaking because they explored complex human emotions and the dark side of the human psyche. His characters were no longer just representations of good or evil—they became fully developed people with internal conflicts.
2: Key Innovations That Transformed Theatre Arts 🎭
Shakespeare didn’t just write plays—he revolutionized the way we think about theatre. His innovations touched nearly every aspect of theatre arts, from storytelling to character development, and even how we perform on stage today. Let’s dive into some of the key contributions that transformed the world of theatre forever.
2.1 Complex Characters: From Archetypes to Real People
Before Shakespeare, characters in plays were often simplistic—good guys were good, and bad guys were bad. Shakespeare flipped this on its head by creating multi-dimensional characters with complex emotions and motivations. Think of Hamlet struggling with indecision, or Macbeth, whose ambition leads him to madness. These characters were no longer just vehicles for the plot; they were people with real, relatable inner turmoil.
2.2 The Power of Soliloquies: Speaking the Inner Mind
One of Shakespeare’s most significant contributions was his use of soliloquies—long speeches where characters speak their innermost thoughts directly to the audience. This technique helped audiences understand a character’s motivations and struggles in a way that hadn’t been done before. Famous soliloquies like “To be or not to be“ in Hamlet or “Out, out, brief candle!” in Macbeth gave audiences a glimpse into the psychological complexity of the characters.
2.3 Dramatic Structure: Mastering the Art of Pacing
Shakespeare didn’t just write stories; he mastered the art of dramatic structure. He introduced the idea of interwoven subplots that enriched the main narrative. Plays like A Midsummer Night’s Dream combine humor, fantasy, and romance, keeping the audience engaged while still advancing the primary storyline. This pacing made Shakespeare’s plays dynamic and exciting, often mixing moments of tension with humor, suspense, and drama.
2.4 Language: Expanding the English Lexicon
Shakespeare’s impact on language is immense—he coined over 1,700 words that we still use today, like “eyeball,” “swagger,” and “lonely.” His ability to play with language made his works more vivid and expressive, adding layers of meaning to every line. Not only did he invent words, but he also used existing words in innovative ways, giving them new meanings and creating memorable expressions.
2.5 Use of Symbolism and Imagery: More Than Just Words
Shakespeare didn’t rely on fancy special effects to tell a story; he used symbolism and imagery in his language to evoke emotions and represent themes. For example, in Macbeth, the recurring imagery of blood represents guilt and the consequences of murder. In Romeo and Juliet, the imagery of light and dark symbolizes the contrasting forces of love and fate.
3: The Influence on Stage Design and Performance Techniques 🎭
Shakespeare’s influence didn’t stop at his writing—he also played a significant role in shaping how theatre looks and feels. From the physical design of the stage to how actors performed, Shakespeare’s innovations transformed the visual and physical experience of theatre. Let’s explore how his contributions helped define modern stage design and performance techniques.
3.1 The Globe Theatre: A Revolution in Stage Architecture
One of the most significant aspects of Shakespearean theatre was the creation of the Globe Theatre, a venue built specifically for his plays. The Globe was different from earlier theatres in several ways:
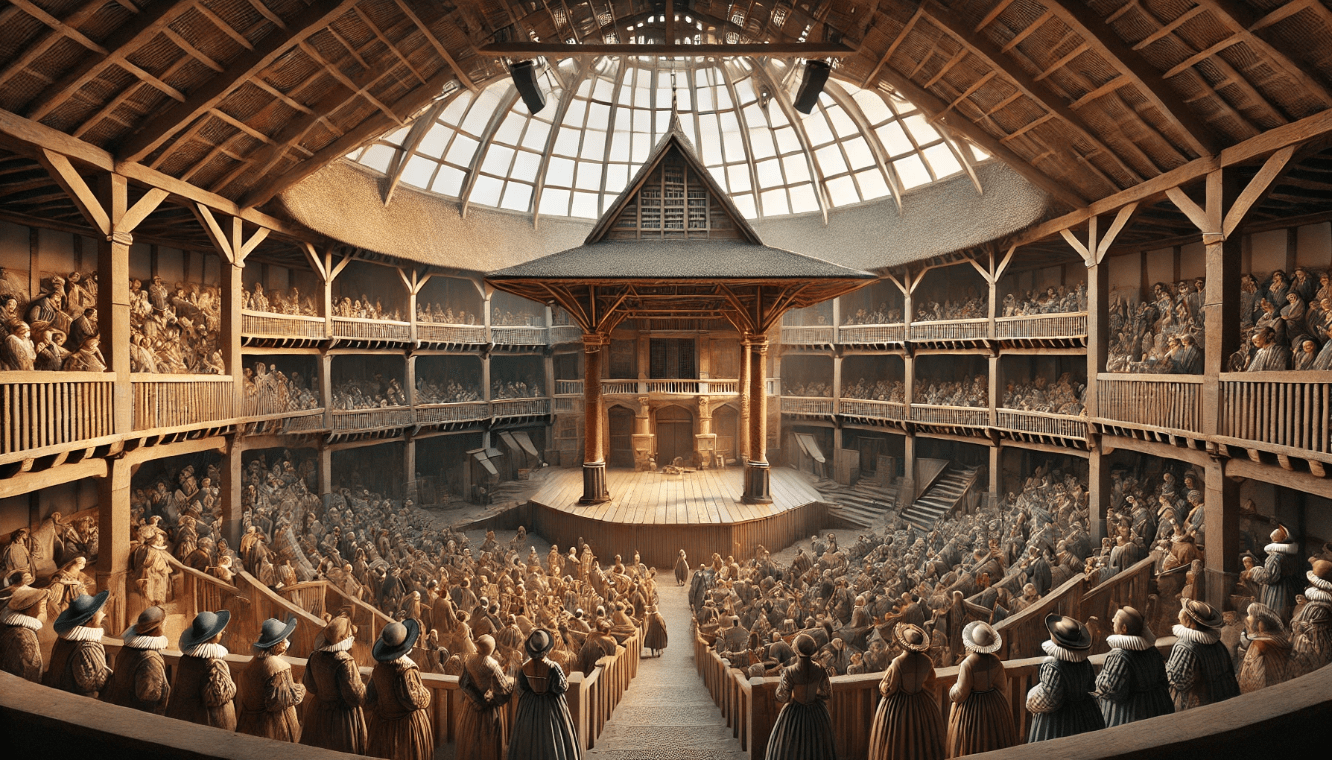
- Thrust Stage: The stage jutted out into the audience, creating a more intimate, immersive experience. This design made the audience feel like they were part of the action.
- Open Roof: With no artificial lighting, performances were staged during the day, utilizing natural light. The open roof also made the experience more dynamic, depending on weather conditions.
- Standing Areas (The Pit): The audience was divided into different sections, with the cheaper seats in the “pit” where people stood close to the actors. This “groundling” experience created an energy that you can still feel in modern performances.
3.2 Minimalism in Stage Design: Focus on the Actors and Words
Shakespeare’s plays were known for their minimalist stage design. Unlike the grand, overly-decorated sets that some might expect, the Globe Theatre and other venues during Shakespeare’s time often had simple props and bare backgrounds. This simplicity allowed the actors’ performances and the language of the play to take center stage.
- Few props and scenery: Instead of elaborate sets, Shakespeare’s works relied on the actors’ creativity to convey time and place. The audience’s imagination was key in creating the world of the play.
- Symbolic use of props: Items like swords, crowns, or costumes were often used symbolically to represent larger themes—something that remains an effective tool in today’s theatre.
3.3 The Role of Costumes in Storytelling
In Shakespeare’s theatre, costumes were not only a way to distinguish characters but also a means of enhancing the storytelling. Actors often wore vibrant, elaborate costumes that reflected their character’s status, personality, and role in the plot. For example:
- Royalty: Kings and queens wore rich, elaborate costumes to indicate their power.
- Commoners: Simple, more modest attire helped distinguish lower-class characters.
Costumes also helped communicate themes and ideas. For instance, in Macbeth, Lady Macbeth’s costumes symbolized her transformation from a powerful figure to someone consumed by guilt and madness.
3.4 Performance Techniques: Engaging the Audience
Shakespeare’s performances were known for their dynamic engagement with the audience. Unlike today’s theatre, where the audience is typically a passive observer, Shakespearean plays encouraged active participation. The audience was physically close to the actors, often reacting out loud and even interacting with them during the performance.
- Direct Address and Interaction: Characters frequently spoke directly to the audience, making them part of the narrative. This kind of interaction was a precursor to modern techniques like breaking the fourth wall.
- Physicality in Acting: The actors relied heavily on their physical presence to convey emotion. Gestures, body language, and voice projection were essential for creating an impact, especially in open-air theatres.
4: Shakespeare’s Impact on Acting and the Acting Profession 🎭
Shakespeare’s influence on acting goes beyond his iconic characters and memorable lines. He transformed the very craft of acting, setting new standards for performance, professionalism, and character portrayal that still resonate today. Let’s explore how his innovations reshaped the acting profession.
4.1 Professionalizing the Actor’s Craft
Before Shakespeare, acting was often seen as an informal or “low” profession. Actors were typically seen as entertainers, not artists. But with the rise of professional theatre companies like the Lord Chamberlain’s Men, Shakespeare helped elevate the status of actors to that of true artists. By establishing a more formal approach to acting, Shakespeare helped turn theatre into a respected profession.
- Full-time acting companies: Shakespeare’s acting troupe was one of the first to offer consistent employment to actors, providing them with steady work and recognition.
- Reputation and legacy: The actors in Shakespeare’s troupe, like Richard Burbage, became legends in their own right. Their performances were considered crucial to the success of the plays, making them stars of their time.
4.2 The Rise of Complex Character Portrayals

Before Shakespeare, many characters in theatre were one-dimensional—good guys versus bad guys. Shakespeare, however, created roles that demanded a deeper understanding of human nature. Characters like Hamlet and Lady Macbeth weren’t just villains or heroes; they were complex individuals with conflicting emotions and inner struggles.
- Psychological depth: Shakespeare’s characters often grapple with moral dilemmas, such as Hamlet’s indecision or Macbeth’s ambition. This complexity required actors to develop a range of emotional skills.
- Character transformation: Shakespeare’s characters often change throughout the play. For example, Lady Macbeth goes from being a strong-willed instigator to a guilt-ridden, broken woman. This transformation was something new in acting.
4.3 Mastery of Language: Voice and Delivery
Shakespeare’s writing required actors to have an exceptional command of language. His use of iambic pentameter, metaphor, and complex dialogue demanded clear enunciation, emotional range, and precision in delivery. Actors were expected to convey deep meaning through their vocal performance, making Shakespeare’s works an excellent training ground for mastering voice and diction.
- Vocal technique: Shakespearean roles often require powerful, emotive speech. The actor must use their voice to convey subtlety, tension, or passion, something that’s essential for today’s actors as well.
- Mastery of language: By working with Shakespeare’s rich, layered text, actors hone their ability to handle complex language in any role they take on.
4.4 Influence on Acting Techniques Today
The way actors perform today can trace much of its roots back to Shakespeare’s time. His work helped shape key aspects of modern acting, such as:
- Emotional honesty: Shakespeare’s characters were grounded in real human emotions, teaching actors to be more authentic in their performances.
- Physicality: Shakespeare’s actors often used exaggerated body movements and gestures to communicate emotions, something that has evolved into the more nuanced physical acting techniques we use today.
- Direct interaction with the audience: Shakespeare’s frequent use of soliloquies and asides blurred the line between actors and their audience, which paved the way for the “breaking of the fourth wall” in modern theatre and film.
5: Shakespeare’s Influence on Modern Theatre Practices
William Shakespeare’s contributions to the world of theatre continue to shape modern performances in profound ways. His innovative approaches to storytelling, character development, and stagecraft have left an indelible mark on how theatre is performed today. Here’s a look at some of the key ways his influence is still felt:
1. Complex Characterization
Shakespeare revolutionized the portrayal of characters. His deep, multifaceted characters, like Hamlet and Lady Macbeth, set a new standard for emotional complexity. Modern actors and directors often look to his works for inspiration when developing rich, layered characters that speak to the human condition. 🎭
2. Language and Dialogue
Shakespeare’s mastery of language gave us memorable lines that transcend time. While he used verse and poetic forms, he also blended them with naturalistic speech. This balance is a key element in modern dialogue, where writers strive to create language that feels both elevated and grounded. ✍️
3. Theatrical Space and Staging
Shakespeare’s plays were originally performed in the open-air Globe Theatre, where the audience was close to the action. This interactive and immersive staging style influences how theatre spaces are designed today. Many contemporary productions aim to break the “fourth wall” and engage audiences directly, just as Shakespeare’s actors did. 🌍
4. Genre Blending
Shakespeare was a master of blending genres, often mixing tragedy with comedy or history with fantasy. This fusion created versatile, multi-layered plays that appealed to wide audiences. Today, theatre productions often incorporate elements from various genres to create more dynamic performances. 🎬
5. Universal Themes
Shakespeare’s exploration of universal themes such as love, jealousy, betrayal, and ambition resonates with people of all cultures and backgrounds. This timeless quality is why his works remain relevant. Today’s theatre continues to reflect these themes, creating performances that feel relatable to diverse audiences across the globe. 🌎
6. Physicality and Movement
Shakespeare’s theatre relied on physicality, as actors had to convey emotions and actions clearly to audiences, especially in open-air spaces. This emphasis on movement and gesture influenced modern performance styles, where body language is just as important as dialogue in conveying a character’s state of mind. 💃
7. Diversity of Roles
Shakespeare expanded the range of roles for actors, both in terms of gender and class. While women were not allowed to perform on stage during his time, Shakespeare wrote parts for female characters that were just as complex as those for men. This inclusivity paved the way for more diverse casting in modern theatre. 🎭
6: Shakespeare’s Legacy Beyond the Stage
William Shakespeare’s influence stretches far beyond the theatre. His impact on literature, language, culture, and even modern entertainment is immense. Let’s explore how his legacy continues to shape our world in various ways:

1. Shaping the English Language
Shakespeare is often credited with coining and popularizing many words and phrases we use today. Terms like “break the ice”, “heart of gold”, and “wild-goose chase” all have their origins in his plays. His creativity with language helped shape English into the rich, expressive language we know today. 📝
Takeaway for Writers & Speakers: Embrace the power of language and experiment with your own creative expressions. Like Shakespeare, think outside the box and create new ways to communicate your ideas!
2. Inspiring Modern Literature
Shakespeare’s works have inspired countless writers, poets, and novelists. His themes of love, betrayal, power, and human nature are still explored in books, movies, and TV shows worldwide. Whether it’s modern adaptations or retellings, Shakespeare’s influence is clear in everything from Hamlet to contemporary novels. 📚
Takeaway for Authors: Draw inspiration from timeless themes. Shakespeare’s works remind us that the most universal emotions and conflicts remain relevant across centuries.
3. Influence on Film and Television
Many movies and TV shows are direct adaptations or loosely based on Shakespeare’s plays. For example, West Side Story draws from Romeo and Juliet, while The Lion King echoes the plot of Hamlet. Filmmakers continue to reimagine his stories for new audiences, blending classic narratives with modern twists. 🎥
Takeaway for Filmmakers and Creatives: Look at Shakespeare’s plots as a foundation for fresh, modern adaptations. You can take his themes and explore them through a new lens, whether it’s in a historical drama or a futuristic setting.
4. Cultural References in Everyday Life
Shakespeare’s influence is also evident in everyday culture. References to his works pop up in speeches, advertisements, and even casual conversations. For instance, when someone says “all the world’s a stage,” they’re quoting As You Like It. These references keep his legacy alive and make his works part of our common cultural vocabulary. 🌍
Takeaway for Marketers & Communicators: Shakespeare’s enduring phrases are an easy way to add depth to your writing and speeches. Use his references to make your messaging resonate more with audiences who appreciate the richness of language.
5. Educational Impact
Shakespeare’s plays remain a cornerstone of educational curricula around the world. Students study his work to understand themes of human nature, history, and society. Beyond the classroom, Shakespeare’s works challenge readers and performers to think critically and engage deeply with literature. 🎓
Takeaway for Educators: Introduce students to Shakespeare not just as a historical figure, but as a tool to explore deeper themes of society and self. Encourage them to see his works as timeless guides for understanding humanity.
6. Philosophical and Psychological Insights
Shakespeare’s exploration of the human condition makes his works relevant to philosophy and psychology. Characters like Hamlet, Macbeth, and Othello give us a glimpse into the complexities of human thought, emotion, and behavior. His characters’ internal struggles continue to be analyzed by scholars for their psychological depth. 🧠
Takeaway for Researchers & Therapists: Shakespeare’s characters offer valuable case studies in psychology. Use his works to gain insights into human motivations and behaviors, and to understand how people respond to power, love, guilt, and ambition.
7. Shakespeare’s Global Reach
Shakespeare’s works have been translated into every major language, making his influence truly global. His stories resonate with people from different cultures because they deal with universal themes like love, revenge, and the quest for power. This cultural reach has solidified his place as a writer for the world, not just for England. 🌎
William Shakespeare’s contributions to the theatre arts are as relevant today as they were centuries ago. His innovative storytelling, complex characters, and mastery of language revolutionized the way we think about performance. Beyond the stage, his influence has permeated literature, film, language, and even modern psychology, solidifying his status as one of the most significant cultural figures in history.
From shaping how we craft narratives to inspiring new forms of artistic expression, Shakespeare’s legacy continues to challenge, entertain, and inspire. Whether you’re a writer, actor, director, or viewer, his works remind us of the power of storytelling to reflect the complexities of the human experience.
By studying his techniques and embracing his themes, modern creators can continue to draw from the rich well of Shakespeare’s work, adapting it to contemporary audiences while keeping the core of his vision alive. His influence is not just a historical artifact but a living, breathing part of the arts that encourages us to explore, express, and connect with each other in meaningful ways. 🌟🎭
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How did Shakespeare influence modern theatre?
Shakespeare revolutionized modern theatre by introducing complex characters, innovative language, and intricate plots. His use of universal themes such as love, power, and betrayal still resonates in contemporary theatre. Many modern plays and performances draw from his unique storytelling techniques, character development, and stagecraft.
2. What are some of Shakespeare’s key contributions to theatre?
Shakespeare’s key contributions include developing realistic, multi-dimensional characters, blending various genres (comedy, tragedy, and history), and enhancing the theatrical experience with rich language and dialogue. His plays also introduced groundbreaking approaches to stage design, including the use of different settings and more dynamic interaction with the audience.
3. How did Shakespeare change the way actors perform?
Shakespeare changed acting by creating roles with deep emotional complexity, allowing actors to explore a wider range of human emotions. His characters like Hamlet and Macbeth require actors to portray psychological depth, leading to more nuanced and powerful performances. Today, actors still look to Shakespeare’s works for inspiration on how to develop complex characters.
4. What impact did Shakespeare’s language have on modern theatre?
Shakespeare’s use of language enriched English by introducing thousands of words and phrases still in use today. His ability to blend poetic verse with natural speech made dialogue more dynamic, inspiring playwrights to experiment with language. Modern theatre often reflects his technique of balancing poetic language with realism to create engaging dialogue.
5. What role did Shakespeare’s themes play in shaping theatre?
Shakespeare’s exploration of universal themes—such as love, jealousy, revenge, and ambition—set the foundation for modern theatre. These timeless themes are still central to contemporary plays, resonating with diverse audiences around the world. His works remind us that exploring human emotions and societal issues can create powerful, relatable stories.
6. How does Shakespeare’s influence extend beyond the stage?
Shakespeare’s influence goes far beyond theatre. His works have shaped literature, film, television, and even popular culture. Many modern movies, TV shows, and novels draw inspiration from his characters, plots, and themes, demonstrating the lasting relevance of his contributions to storytelling.
7. How can modern theatre artists apply Shakespeare’s techniques today?
Modern theatre artists can apply Shakespeare’s techniques by creating complex, relatable characters and experimenting with multi-genre storytelling. They can also draw from his dynamic use of language and physicality to create immersive, engaging performances. Exploring themes of love, conflict, and power, much like Shakespeare did, helps modern artists connect with audiences on a deeper level.
8. What is Shakespeare’s legacy in contemporary performance?
Shakespeare’s legacy in contemporary performance is seen in how his plays continue to be adapted, performed, and reimagined globally. His focus on human complexity, his innovative language, and his influence on character development remain central to theatre today. His works serve as both a source of inspiration and a model for modern playwrights, directors, and performers.
