Exploring the Impact of Shakespeare on Elizabethan Theatre: How His Work Shaped the Stage and Revolutionized Drama
Shakespeare’s influence on the world of theatre is nothing short of revolutionary. 
In this article, we’ll dive deep into how Shakespeare’s innovations in character development, storytelling, and stage design left a lasting imprint on not just his era, but on theatre as we know it today. Whether you’re a budding playwright, a theatre enthusiast, or just curious about the roots of modern drama, understanding the impact of Shakespeare on Elizabethan theatre is essential. Ready to uncover how his genius reshaped the world of performance forever? Keep reading to discover more!
Table of Contents
Toggle1.The Evolution of Elizabethan Theatre Before Shakespeare
Before Shakespeare’s meteoric rise to fame, Elizabethan theatre was quite different from the bustling, complex performances we know today. 
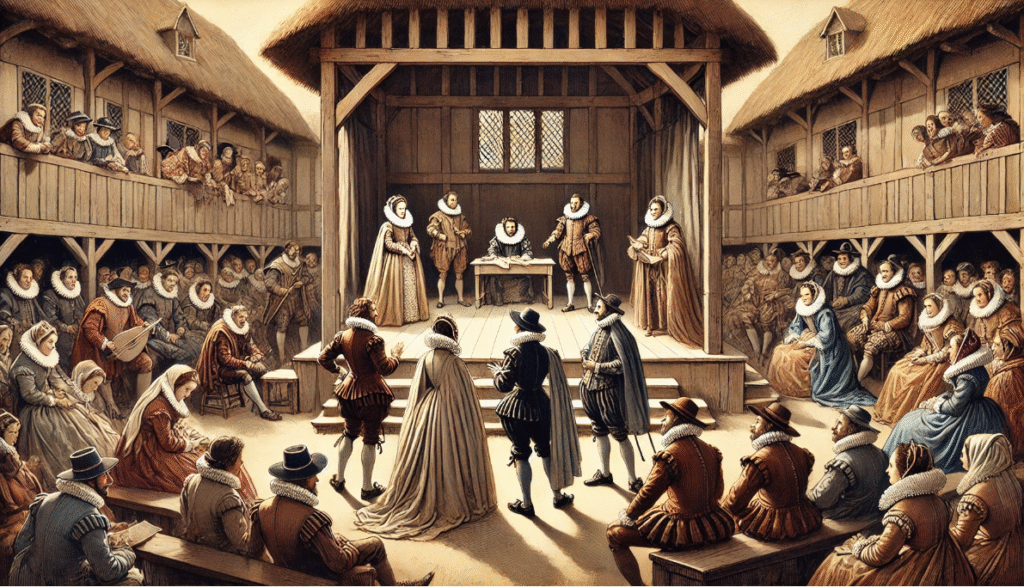
Theatrical Beginnings: Religious and Morality Plays
In the early years of Elizabethan theatre, plays were often rooted in religious messages or moral lessons. These performances were typically staged in churches or town squares, with the aim of educating the audience on good behavior, the consequences of sin, and the virtues of the Christian faith.
- Mystery Plays: Based on biblical stories, these plays often featured elaborate sets and multiple characters. Their primary purpose was to teach religious values and entertain, but they didn’t delve much into character complexity or nuanced themes.
- Morality Plays: These plays were a step closer to drama as we know it today. They used allegorical characters, such as Everyman, to represent moral choices and virtues. While they introduced more character-driven narratives, these plays still kept things fairly black and white.
The Rise of Public Theatres
By the late 16th century, the landscape of theatre was beginning to change. Public playhouses like The Theatre and The Rose started appearing in London. These venues welcomed large audiences from all walks of life, from nobility to common folk, making theatre more accessible than ever before.
- Stage Design: The stage was basic, often just a raised platform with minimal props. The emphasis was still on dialogue, as the limited set design couldn’t carry the weight of elaborate scenery or props. The audience relied heavily on the actors’ performances to bring the story to life.
- Types of Performances: At this time, plays were still largely influenced by medieval traditions, though playwrights like Christopher Marlowe were beginning to push boundaries with more sophisticated language and drama.
Enter Shakespeare: The Game-Changer
While early Elizabethan theatre was primarily concerned with religious or moral lessons, the stage was ready for something new—a revolution in storytelling. Shakespeare didn’t just step onto this landscape; he transformed it.
- His characters were not simply representations of virtues or vices. They were fully realized, complex individuals, full of contradictions and depth. This shift allowed audiences to relate to the characters on a much deeper level, making theatre a more personal experience.
- Shakespeare also introduced a more sophisticated use of language, blending poetry with everyday speech. This not only raised the standard of writing but also helped elevate English as a language of artistic expression.
In short, before Shakespeare’s influence, Elizabethan theatre was a space for simple, moral lessons, with limited character development and storytelling. Shakespeare changed that forever by bringing a new depth to both the structure of the plays and the characters themselves, laying the groundwork for modern drama as we know it today.
2. Shakespeare’s Innovations: Transforming the Stage
When Shakespeare entered the scene, Elizabethan theatre was already evolving. However, his contributions took it to an entirely new level. 
1. Complex Characters: Moving Beyond the Stereotypes
Before Shakespeare, many characters in plays were simple, one-dimensional figures, often representing virtues or vices. Shakespeare changed that by creating characters with depth, contradictions, and internal struggles.

- Character Development: Shakespeare’s characters, such as Hamlet, Macbeth, and Lady Macbeth, were complex, often grappling with deep moral dilemmas and psychological conflicts. These characters felt real, with flaws, desires, and weaknesses that audiences could relate to on a personal level.
- Layered Motivations: Unlike the purely good or bad characters of previous plays, Shakespeare’s protagonists had multifaceted personalities. For example, in Macbeth, the titular character’s ambition, guilt, and paranoia make him a compelling figure that audiences could empathize with, despite his moral downfall.
This shift from flat characters to multi-dimensional individuals is one of Shakespeare’s greatest contributions to the stage. It laid the groundwork for modern character-driven storytelling.
2. Plot Complexity: Weaving Multiple Themes and Stories
Shakespeare’s plots were anything but simple. He wove multiple themes, subplots, and conflicts into his plays, creating a rich tapestry of drama.
- Interwoven Subplots: Many of Shakespeare’s plays, such as King Lear and Twelfth Night, feature complex subplots that parallel the main story, adding layers of intrigue and emotional depth.
- Thematic Depth: Shakespeare explored universal themes like love, betrayal, ambition, and the human condition. In Romeo and Juliet, for instance, love is portrayed not just as a romantic ideal but as something that can lead to tragedy due to family conflict and societal constraints.
These complex narratives and the way Shakespeare intertwined various elements of plot gave his plays a timeless quality, making them relevant across different cultures and eras.
3. The Use of Soliloquy: Giving Characters a Voice
One of Shakespeare’s most revolutionary techniques was his use of soliloquy—speeches where characters express their inner thoughts directly to the audience.
- Emotional Insight: Through soliloquies, characters like Hamlet and Macbeth shared their internal struggles, giving audiences an intimate look into their psychological states. This technique deepened the emotional connection between the audience and the characters.
- Philosophical Reflection: These speeches often provided not just emotional insight but also philosophical reflections on life, death, morality, and human nature. Hamlet’s famous “To be or not to be” soliloquy, for example, is a profound meditation on existence that resonates with audiences even today.
Soliloquies became a powerful tool in the actor’s arsenal, allowing for moments of deep reflection and connection with the audience. It wasn’t just about speaking the lines—it was about connecting emotionally and intellectually.
4. Rich Language: Elevating Dialogue to Art
Shakespeare’s use of language was unlike anything that had come before. He elevated everyday speech into something poetic and profound, often creating new words and expressions that are still in use today.
- Poetry and Prose: Shakespeare skillfully balanced verse (poetry) and prose in his plays. While characters of noble birth often spoke in verse, lower-class characters spoke in prose, which helped define their social status. This not only made the dialogue more dynamic but also added a layer of realism to his plays.
- Wordplay and Wit: Shakespeare’s plays are filled with puns, metaphors, and clever wordplay. These literary devices added humor, complexity, and richness to the dialogue. His witty exchanges, such as those between Beatrice and Benedick in Much Ado About Nothing, continue to delight audiences.
Shakespeare’s linguistic innovation transformed theatre from simple storytelling to a more refined art form, where language itself became a tool for emotional and intellectual expression.
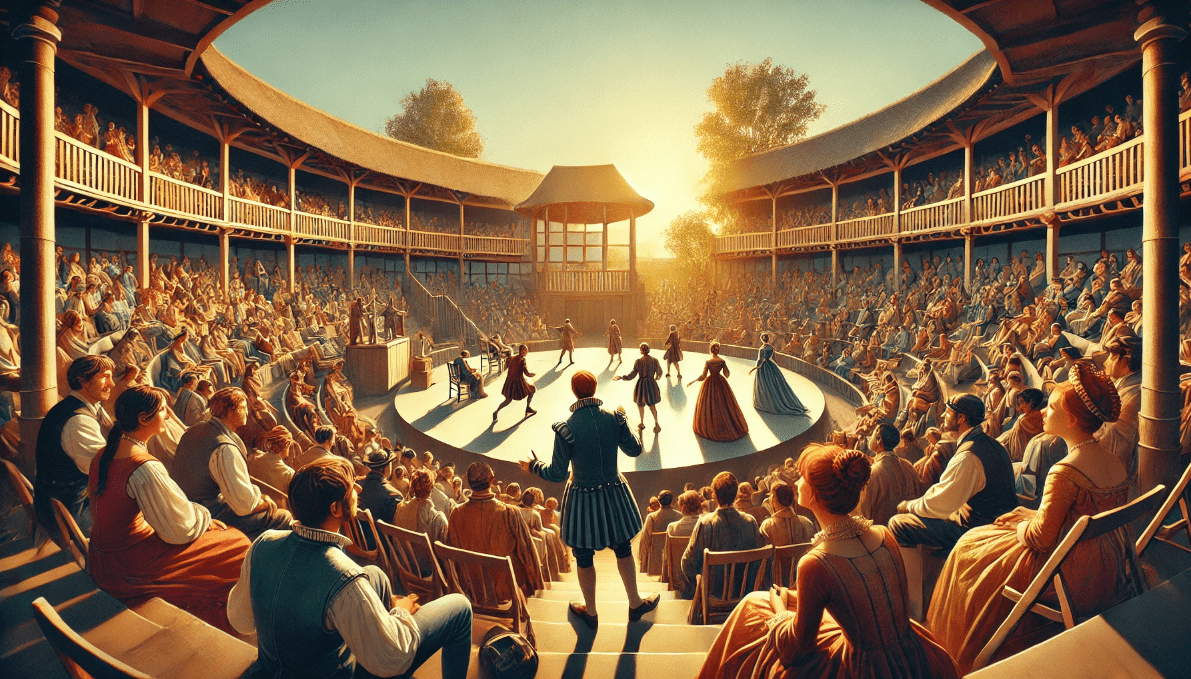
5. Stage Design: Emphasizing Minimalism and Imagination
While Shakespeare’s writing was groundbreaking, so was the way his plays were performed. The Globe Theatre, where many of his plays were staged, embraced a minimalist approach to stage design.
- Open-Air Theatre: The Globe was an open-air theatre, with a circular design that allowed for maximum audience engagement. The actors performed on a simple stage, often with little more than basic props and costumes to suggest location and time.
- Imagination Over Sets: With few set pieces, the audience had to use their imagination to transport themselves into the world of the play. This forced a more intense focus on the actors’ performances and the storytelling itself.
By stripping away the distractions of elaborate sets, Shakespeare’s theatre emphasized the power of the story and the actors’ craft. It’s an approach that still influences modern theatre and film today, where minimalism often drives deeper emotional and narrative engagement.
3. Shakespeare’s Role in Shaping Theatre Structure
When we think about Shakespeare’s influence on theatre, we often focus on his groundbreaking writing. However, his impact on the physical structure of theatre is just as significant. 
1. The Globe Theatre: A Revolutionary Space
The Globe Theatre, where many of Shakespeare’s plays were performed, was more than just a venue—it was a reflection of his innovative approach to theatre structure.
- Open-Air Design: Unlike enclosed theatres, the Globe was an open-air structure, which allowed for natural light and an immersive experience. This design encouraged a direct connection between the actors and the audience, making the performance feel more immediate and interactive.
- The Circular Stage: The Globe’s stage was circular, allowing actors to engage with audiences from all sides. This unique shape helped create a dynamic relationship between the performers and the spectators, breaking down the barrier between them.
- The Pit and Gallery: The audience was divided into different sections. The “pit” at the front was for standing room, where the working-class “groundlings” could watch the play for a lower price. The galleries, for wealthier patrons, offered a more comfortable view. This structure made theatre more accessible to all social classes.
2. Minimalism on Stage: Imagination Takes the Lead
Shakespeare’s use of minimalistic stage design was a game-changer. With few props and basic sets, the focus shifted entirely to the actors’ performances and the audience’s imagination.
- Sparse Set Pieces: The Globe Theatre featured a simple stage with minimal decoration. A few props, a trapdoor, and some costumes were all that was needed to transport the audience into different worlds. This forced both the actors and the audience to engage more deeply with the story being told.
- Audience Engagement: With no elaborate sets to rely on, Shakespeare’s plays encouraged audiences to use their imagination to fill in the gaps. This minimalistic style focused attention on the language and characters, making the experience more personal and intimate.
3. The Role of the Actor: Breaking the Traditional Mold
Shakespeare’s theatre structure also revolutionized the role of the actor, emphasizing their ability to perform and connect with the audience in new ways.
- A Greater Range of Roles: The Globe allowed actors to perform a wide variety of roles, from kings to commoners, using minimal props and costume changes. This flexibility encouraged greater acting skill and range. Actors weren’t limited by costumes or props but were instead challenged to convey the essence of their characters through performance alone.
- Audience Interaction: The design of the Globe, with its open structure and circular stage, allowed actors to interact more directly with the audience. Performers could engage with the crowd, move around the stage, and even improvise, creating a more lively and reactive environment. This interaction helped elevate the overall theatre experience, making it feel less like a formal event and more like a shared experience between actors and spectators.
4. Changing the Way Theatre Was Experienced
Shakespeare’s theatre innovations didn’t just change the performance itself; they transformed the very experience of theatre-going.
- Accessible to All: The division of the Globe’s seating made theatre accessible to a broader audience. The “groundlings,” who stood in the pit, were often the most vocal and engaged members of the audience, while the wealthy patrons in the galleries enjoyed a more comfortable experience. This social mix created a vibrant and dynamic atmosphere, where everyone could enjoy the play, regardless of their social status.
- A Focus on Performance: With fewer distractions, the audience’s attention was entirely focused on the actors and the story. The minimalistic approach to stage design made the performance itself the star of the show, placing importance on dialogue, character interaction, and emotion rather than flashy sets or effects.
5. Lasting Influence on Modern Theatre
Shakespeare’s role in shaping theatre structure continues to influence modern theatre and cinema. 
- The Influence of the Open Stage: Modern theatres still embrace elements of the open stage, where actors can engage with the audience and create a more immersive experience. This approach is seen in many contemporary productions, where the boundaries between the audience and performers are often blurred.
- Minimalist Set Design: Many modern productions, both in theatre and film, use minimalist sets to focus more on character development and storytelling. This reflects Shakespeare’s belief that the power of the performance lies in the actors and the words, not in elaborate decorations.
4. Thematic Innovations: How Shakespeare Changed Drama Forever
Shakespeare didn’t just transform the structure and performance of theatre—he completely revolutionized the way stories were told. 

1. Universal Themes: Connecting Across Time and Culture
One of Shakespeare’s greatest achievements was his ability to tackle universal themes that speak to the human experience—no matter the time period or culture.
- Love and Passion: From the tragic romance of Romeo and Juliet to the complex relationships in Much Ado About Nothing, Shakespeare explored the many facets of love—both its beauty and its potential for destruction. These portrayals of love transcend cultural boundaries, making his plays relatable to any audience, at any time.
- Ambition and Power: In plays like Macbeth and Julius Caesar, Shakespeare delves into the corrupting influence of ambition and the consequences of unchecked power. These themes still resonate with modern audiences, particularly in political dramas and contemporary stories about power struggles.
- Revenge and Justice: Themes of revenge and justice are explored in works like Hamlet and Titus Andronicus. Shakespeare’s characters wrestle with moral dilemmas, questioning what is right and what is just in a world full of betrayal and deceit. These themes raise ethical questions that are just as relevant today.
Shakespeare’s ability to explore timeless human emotions and struggles made his works incredibly powerful, allowing them to transcend the specific context of Elizabethan England.
2. Moral Ambiguity: Embracing Complexity
Shakespeare’s characters were rarely one-dimensional. Instead, they were morally complex, grappling with internal conflicts and imperfections.
- Tragic Heroes: Characters like Hamlet, Macbeth, and Othello are not simply villains or heroes—they are deeply flawed individuals whose actions and decisions are shaped by internal struggles. This moral ambiguity invites the audience to sympathize with characters who might otherwise be viewed as irredeemable.
- Complex Motivations: Shakespeare introduced characters who acted out of conflicting desires, such as love, ambition, and guilt. In Macbeth, for example, the title character’s internal battle between ambition and conscience drives the plot, making him a tragic figure rather than just a villain.
This exploration of moral complexity was groundbreaking. It shifted the focus from simple, clear-cut characters to nuanced individuals who felt real and relatable. This approach has since influenced countless writers and filmmakers, who now use complex characters to add depth to their stories.
3. Human Nature: Deep Psychological Insight
Shakespeare had an unparalleled understanding of human nature. His plays often explore the depths of human emotion, psychology, and motivation.
- Psychological Depth: Shakespeare’s characters are not just plot devices—they are people with fears, desires, and deep psychological complexities. In Hamlet, the protagonist’s soliloquies give us a glimpse into his troubled mind, full of existential doubt and internal conflict. In Macbeth, we see how unchecked ambition can spiral into madness and paranoia.
- Internal Conflict: Shakespeare masterfully captured the internal struggles of his characters, particularly in his tragedies. This focus on psychological realism was ahead of its time, influencing the development of modern psychology and even contemporary literature, where internal conflict is central to character development.
Shakespeare’s exploration of the human psyche was groundbreaking, offering insights into personal motivations, moral dilemmas, and emotional struggles that still feel relevant to today’s audiences.
4. Social Commentary: Addressing Power, Class, and Gender
Shakespeare was not afraid to tackle issues of class, power, and gender, using his plays as a mirror to reflect the social norms and inequalities of his time.
- Class and Social Hierarchy: In plays like King Lear and Taming of the Shrew, Shakespeare critiques the rigid class structures of Elizabethan society. In King Lear, for example, the distribution of power and wealth among the royal family leads to betrayal and chaos. The play questions the fairness of such power structures and the impact they have on individuals.
- Gender Roles: Shakespeare often explored gender dynamics, particularly through strong female characters like Lady Macbeth in Macbeth and Portia in The Merchant of Venice. These characters challenge traditional gender roles, displaying both strength and vulnerability. By doing so, Shakespeare raised important questions about the role of women in society, making his plays a subtle form of social commentary.
By addressing these themes, Shakespeare not only entertained but also prompted audiences to reflect on their own social and political realities.
5. The Supernatural and the Unexplained
Shakespeare’s use of the supernatural and unexplained forces in his plays added an element of mystery and wonder that captivated audiences.
- Witches and Prophecies: In Macbeth, the appearance of the three witches and their cryptic prophecies serve as a catalyst for Macbeth’s descent into madness. The supernatural elements symbolize the unknown forces that influence human behavior, adding layers of complexity to the story.
- Spirits and Ghosts: In Hamlet, the ghost of the king sets the stage for the central conflict, motivating Hamlet to avenge his father’s death. This supernatural presence deepens the play’s exploration of revenge, guilt, and justice.
5. Shakespeare’s Influence on Acting and Performance Styles

Shakespeare’s impact on acting and performance styles cannot be overstated. 
1. A Shift to Emotional Depth and Realism
Before Shakespeare, acting was often more about delivering lines than expressing deep emotions. Actors typically performed in a more stylized, formal manner. However, Shakespeare’s complex characters demanded a shift toward realism.
- Emotional Range: Shakespeare’s characters are multifaceted, with deep internal struggles and conflicting desires. Hamlet’s existential dilemma, Macbeth’s growing paranoia, and Juliet’s impassioned love required actors to explore a range of emotions. This focus on emotional depth challenged actors to move beyond surface-level performances and truly connect with their characters’ psychological complexity.
- Realistic Portrayal: Shakespeare introduced a style of acting that emphasized realism—characters were no longer just archetypes or symbolic figures. They became real people with complex emotions and motivations, encouraging actors to perform with more nuance and subtlety.
This shift to emotional depth in acting was groundbreaking. It encouraged actors to explore characters from the inside out, making each performance feel authentic and personal.
2. The Rise of the “Method” Approach to Acting
Shakespeare’s writing opened the door to what would later become known as method acting—a style that focuses on emotional authenticity and drawing from personal experience.
- Inner Motivation: Shakespeare’s characters are driven by powerful internal motivations, whether it’s Hamlet’s desire for revenge or Lady Macbeth’s ambition. To accurately portray these characters, actors had to dig deep into their own emotions and experiences, fostering a greater connection to the roles they played.
- Character Transformation: In order to bring Shakespeare’s characters to life, actors had to undergo a transformation, adopting not only the character’s speech but also their thoughts, feelings, and physicality. This concept of fully embodying a role laid the foundation for modern acting techniques, where actors are encouraged to immerse themselves in their character’s world.
The idea of “becoming” the character, rather than simply acting the part, has had a lasting effect on performance styles worldwide.
3. The Importance of Physicality and Movement
Shakespearean acting wasn’t just about delivering lines—it was about becoming the character through movement, posture, and physical presence.
- Expressive Movement: Shakespeare’s plays often called for dramatic, physical performances. For instance, Macbeth’s intense ambition is conveyed not only through his speech but also through his posture and physical actions. The actors had to use their bodies to communicate the character’s emotional state and journey.
- Interaction with the Audience: The open stage of the Globe Theatre allowed for direct interaction with the audience, requiring actors to project their voices and use exaggerated physical gestures. This style of performance made the actors’ movements larger and more dynamic, ensuring they could capture the attention of the audience, even from a distance.
Physicality became an essential part of Shakespearean performance, contributing to the larger-than-life quality that made his plays so engaging.
4. The Role of the Chorus: Narration and Commentary
Shakespeare often used a chorus or narrator to help set the tone of the play and guide the audience through the story.
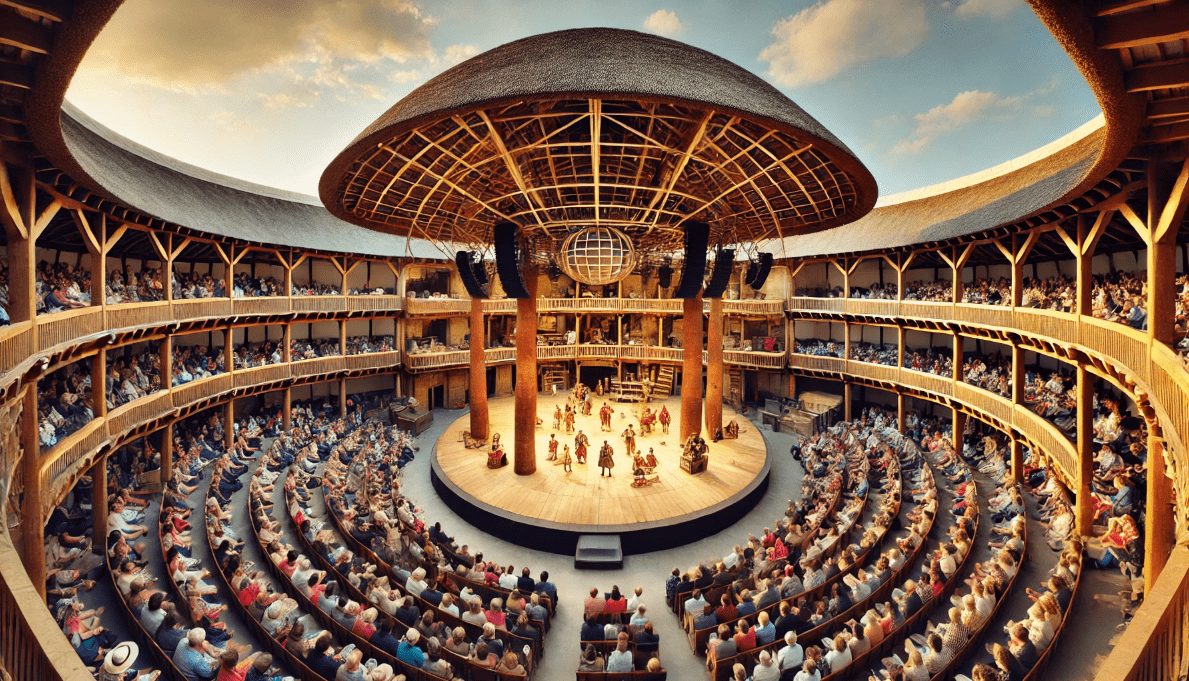
- Choral Influence: In plays like Henry V, the Chorus addresses the audience directly, commenting on the action and setting the stage. This role often gave the audience context or highlighted key moments in the story. The use of a chorus helped bridge the gap between the audience and the action, making it easier to follow complex plots.
- Breaking the Fourth Wall: Shakespeare’s use of direct address blurred the line between actors and audience. By speaking directly to the audience, characters could share their thoughts or offer insights into the unfolding drama. This technique made the audience feel more involved in the performance, as if they were part of the narrative.
The use of a chorus and breaking the fourth wall in this way helped establish a more interactive and engaging theatrical experience, something we still see in modern productions today.
5. The Lasting Influence on Modern Theatre and Film
Shakespeare’s contributions to acting and performance styles didn’t stop with his own time. His innovations continue to shape modern theatre and film.
- Character Complexity: Modern actors, whether on stage or in film, still look to Shakespearean characters as models for depth and complexity. Characters in contemporary drama, from antiheroes to tragic figures, owe a great debt to Shakespeare’s richly developed roles.
- Method Acting: Techniques developed through Shakespeare’s writing have directly influenced the development of method acting, popularized by actors like Marlon Brando and Robert De Niro. This approach emphasizes emotional truth and deep character immersion, echoing Shakespeare’s own emphasis on emotional authenticity.
- Physical Expression in Performance: The larger-than-life performances required for Shakespeare’s plays still influence how actors approach roles in both theatre and film. From exaggerated gestures to powerful stage presence, Shakespeare’s emphasis on physicality continues to guide actors in creating dynamic, memorable performances.
6. The Global Legacy: Shakespeare’s Influence Beyond Elizabethan Theatre
Shakespeare’s impact wasn’t confined to the stages of Elizabethan England; his legacy stretches across the globe, influencing theatre, literature, and culture in profound ways. 
1. Shakespeare’s Plays in Modern Theatre and Film
Shakespeare’s works are among the most performed plays worldwide, continuing to captivate audiences with their timeless themes and rich characters.
- Global Reach: His plays have been translated into every major language and performed in countries around the world. Whether in the West End, Broadway, or local theatres, his works remain staples of the stage, drawing new audiences and inspiring fresh interpretations.
- Film Adaptations: Countless films have been based on Shakespeare’s plays. For instance, West Side Story is a modern retelling of Romeo and Juliet, while The Lion King draws heavily from Hamlet. These adaptations take Shakespeare’s universal themes of love, betrayal, power, and fate and apply them to contemporary settings, proving the relevance of his ideas in modern storytelling.
Shakespeare’s influence on film and theatre ensures that his works continue to be a source of inspiration for writers, directors, and actors today.
2. Shaping Literature and Language
Shakespeare’s contributions to literature and language are monumental.
- Vocabulary and Expressions: Shakespeare is credited with coining or popularizing over 1,700 words and phrases that are still in use today. Common expressions like “break the ice,” “wild-goose chase,” and “heart of gold” all originated from his works. His creative use of language helped shape modern English and expanded its expressive range.
- Literary Influence: Many of the world’s greatest writers, including Charles Dickens, James Joyce, and modern playwrights, have drawn inspiration from Shakespeare’s themes, character development, and language. His ability to blend high drama with accessible language made his works a bridge for future generations of writers, enriching the entire literary world.
Through his inventive use of language, Shakespeare left an enduring legacy on the way we speak and write today.
3. Shakespeare and Popular Culture
Shakespeare’s influence extends far beyond formal theatre and literature into popular culture.
- Movies, TV, and Music: Many films, TV shows, and even songs are influenced by Shakespeare’s works. For example, the TV series Shakespeare in Love imagines a fictional account of Shakespeare’s life, while shows like The Simpsons often feature Shakespearean references and parodies. Additionally, artists like Bob Dylan have cited Shakespeare as an influence in their lyrics.
- Cultural References: From literature to social media, Shakespeare’s plays are frequently referenced in everyday conversations, books, and movies. His characters and themes have become a part of our collective cultural vocabulary, showing how deeply embedded his influence is in global society.
Shakespeare’s reach extends into nearly every corner of modern entertainment, making his work an enduring part of our cultural fabric.
4. The Universality of Shakespeare’s Themes
What makes Shakespeare’s legacy so powerful is the universality of his themes.
- Human Emotions and Relationships: Shakespeare’s exploration of love, jealousy, ambition, guilt, and power resonates with people from all walks of life. His characters’ struggles are just as relatable today as they were in the 16th century, which is why his plays continue to captivate audiences from all cultures and backgrounds.
- Cultural Relevance: Shakespeare’s plays have been adapted to fit various cultural contexts, from Japanese Kabuki theatre adaptations of Macbeth to African versions of Hamlet. His exploration of universal human experiences allows his work to be reinterpreted and understood across diverse societies.
Shakespeare’s ability to address fundamental aspects of the human condition is what keeps his work relevant in every corner of the globe.
5. Educational Legacy
Shakespeare’s influence extends to education, where his works are often central to literature curricula around the world.
- Studied Worldwide: Shakespeare’s plays are taught in schools, universities, and drama programs worldwide. His texts provide valuable insights into language, history, psychology, and the human experience, making them key educational tools in understanding both literary traditions and cultural history.
- Global Shakespeare Festivals: Every year, countries across the globe host Shakespeare festivals, where his plays are performed in various languages, interpretations, and styles. These festivals celebrate Shakespeare’s contributions to theatre and serve as a reminder of his lasting impact on global culture.
Through education and academic study, Shakespeare’s work continues to influence the minds of students and scholars worldwide.
7. Practical Takeaways: What Can We Learn from Shakespeare Today?
Shakespeare’s contributions to theatre and drama are vast, but what can we take from his work and apply to our lives today? His themes, storytelling techniques, and approach to language still have practical lessons to offer. 

1. Embrace Complexity in Characters and Storytelling
One of Shakespeare’s greatest strengths was his ability to create complex, multi-dimensional characters. 
- Practical Tip: In your own work, make sure to develop characters that have strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, and internal conflicts. When characters feel real, the audience will connect with them on a deeper level, just as Shakespeare’s characters do.
- Why It Works: Characters with depth and complexity engage the audience, creating a more memorable experience. They invite empathy and spark thoughtful reflection, which is why Shakespeare’s characters continue to resonate centuries later.
2. The Power of Language and Wordplay
Shakespeare’s use of language was revolutionary. He played with words, creating rich metaphors, puns, and rhythms that gave his plays a distinctive flair.
- Practical Tip: In your writing or communication, experiment with language. Use metaphors, vivid imagery, and powerful word choices to evoke emotion or add layers of meaning. Pay attention to rhythm and sound as well; even the flow of words can have a significant impact.
- Why It Works: Language can be a powerful tool for creating emotional connections. Whether it’s a speech, a piece of writing, or even a business presentation, Shakespeare’s mastery of language teaches us that the right words can change minds and captivate hearts.
3. Explore Universal Themes
Shakespeare’s plays continue to resonate because they address themes that are universal—love, betrayal, ambition, power, and the human condition. 
- Practical Tip: In whatever field you’re working—whether it’s writing, business, or personal relationships—consider the universal themes that underpin your work. Reflect on the timeless struggles people face and weave them into your narratives or strategies to make them more relatable and impactful.
- Why It Works: Universal themes are not bound by time, place, or culture. They connect people from different backgrounds and resonate on a deeper level. Shakespeare’s ability to tap into these themes is part of why his works remain so powerful today.
4. Embrace the Human Condition with Empathy
One of the most striking aspects of Shakespeare’s plays is his exploration of human emotions, flaws, and vulnerabilities. He didn’t shy away from the messy, complicated parts of being human.
- Practical Tip: Practice empathy in your daily life and work. Understand that people’s actions are often motivated by their emotions, past experiences, and internal struggles. Use this understanding to create stronger relationships or develop more nuanced projects.
- Why It Works: Shakespeare’s ability to portray the full range of human experience with empathy helps make his work timeless. In our own lives, understanding the complexity of human nature allows us to navigate relationships and challenges more effectively.
5. Use Conflict to Drive Your Story Forward
Whether it’s internal conflict within a character or external conflict between characters, Shakespeare knew that drama is driven by tension. His works are filled with characters who struggle with moral dilemmas, personal desires, and outside pressures.
- Practical Tip: In storytelling, whether on stage or in your professional life, use conflict to drive the narrative. Conflict creates interest, sparks emotional engagement, and ultimately pushes the story or action forward.
- Why It Works: Conflict introduces drama and keeps audiences invested. In business, for example, understanding and addressing conflicts or challenges can help you solve problems and innovate solutions. In personal storytelling, conflict creates the tension necessary to captivate your audience.
6. The Value of Simplicity in Performance
Shakespeare’s stage design was minimal, yet the performances were anything but simple. His works prove that you don’t need flashy sets or overwhelming visuals to tell a powerful story—what matters most is the depth of the performance and the clarity of the message.
- Practical Tip: In presentations, writing, or even daily conversations, focus on clarity and substance rather than unnecessary embellishments. Sometimes, less is more—make sure your core message stands out.
- Why It Works: When you simplify the presentation, you make it easier for your audience to connect with the true essence of your message. Whether in writing or speaking, clear communication often leaves a stronger impact than over-complicating things.
7. Reinventing the Old: Adaptation and Relevance
Shakespeare’s works have been adapted for modern times, proving that old stories can be made fresh and relevant.
- Practical Tip: Don’t be afraid to reinterpret old ideas, stories, or concepts in new and relevant ways. Whether it’s updating a classic idea for modern times or adding your own twist to an existing project, adaptation is a great way to keep things engaging and innovative.
- Why It Works: Reinvention allows you to breathe new life into the familiar, making it feel fresh and exciting. Just as West Side Story reimagined Romeo and Juliet, you can create something new from something old by giving it new context or perspective.
Shakespeare’s Lasting Lessons
Shakespeare’s work isn’t just for scholars and theatre enthusiasts—it offers practical insights that can be applied in all aspects of life, from personal development to business to creative work. By embracing complexity in characters, experimenting with language, exploring universal themes, and understanding human nature, we can all draw inspiration from the master playwright. 
Shakespeare’s Lasting Impact on Theatre and Beyond
William Shakespeare’s influence on Elizabethan theatre is undeniable, and his legacy has only grown stronger over the centuries. 
As we’ve explored throughout this article, Shakespeare’s contributions went far beyond the stage. He crafted universal themes that connect us all, from love and betrayal to ambition and power. His characters are as relatable today as they were in his own time, and his mastery of language and storytelling continues to inspire writers, directors, and creatives of all kinds.
Shakespeare’s impact extends into every corner of modern life—teaching us the power of emotional depth, the importance of conflict, and the value of human connection. By applying his insights to our own work, whether in business, art, or personal relationships, we can learn to communicate more effectively, tell more compelling stories, and connect with others on a deeper level.
As you reflect on the profound impact of Shakespeare, consider how you can incorporate his lessons into your own life. His work remains a timeless treasure—one that continues to teach, inspire, and enrich us.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How did Shakespeare influence the development of Elizabethan theatre?
Shakespeare revolutionized Elizabethan theatre by introducing complex characters, intricate plots, and innovative use of language. His works emphasized realism and emotional depth, moving beyond the simplistic religious and morality plays that dominated before him. His influence also extended to stage design and audience interaction, changing how plays were both performed and experienced.
2. What makes Shakespeare's characters so important in theatre?
Shakespeare’s characters were groundbreaking because they were complex and multi-dimensional. Unlike previous one-dimensional figures, his characters—like Hamlet, Macbeth, and Juliet—grapple with internal conflicts, making them more relatable and emotionally resonant. This depth has influenced countless storytellers, both in theatre and beyond, to create more realistic, human characters.
3. How did Shakespeare's writing impact the English language?
Shakespeare’s works contributed significantly to the development of the English language. He introduced over 1,700 new words and countless expressions still used today, such as “break the ice,” “wild-goose chase,” and “heart of gold.” His creative use of language made English more versatile and expressive, influencing both literature and everyday speech.
4. What was the role of the Globe Theatre in Shakespeare’s work?
The Globe Theatre was central to Shakespeare’s success, providing a unique platform for his plays. Its open-air, circular design allowed for more audience interaction, with actors performing on a minimalistic stage that focused attention on the story and characters. This innovative approach to stage design set the standard for modern theatre.
5. How did Shakespeare influence modern theatre and film?
Shakespeare’s influence on modern theatre and film is immense. Many contemporary films and TV shows are adaptations of his plays, such as West Side Story (based on Romeo and Juliet) and The Lion King (based on Hamlet). His exploration of timeless themes like love, betrayal, and power continues to inspire storytellers worldwide, making his works universally relatable.
6. Why are Shakespeare’s themes still relevant today?
Shakespeare’s themes are timeless because they explore fundamental aspects of human nature. His works address love, ambition, betrayal, justice, and the complexities of the human condition—topics that remain just as pertinent today as they were in his time. This universal relevance is why his plays continue to resonate with audiences across cultures and generations.
7. How did Shakespeare change acting and performance styles?
Shakespeare transformed acting by emphasizing emotional depth and realism. His complex characters required actors to delve into their roles more deeply, focusing on both inner conflict and external performance. This focus on emotional authenticity helped pave the way for modern acting techniques like method acting.
8. What lessons can we learn from Shakespeare’s works today?
Shakespeare’s works teach us the value of complexity in storytelling, the power of language, and the importance of empathy and emotional depth. Whether in writing, business, or relationships, his ability to create compelling narratives with universal themes and deep characters provides timeless lessons on communication and connection.




















