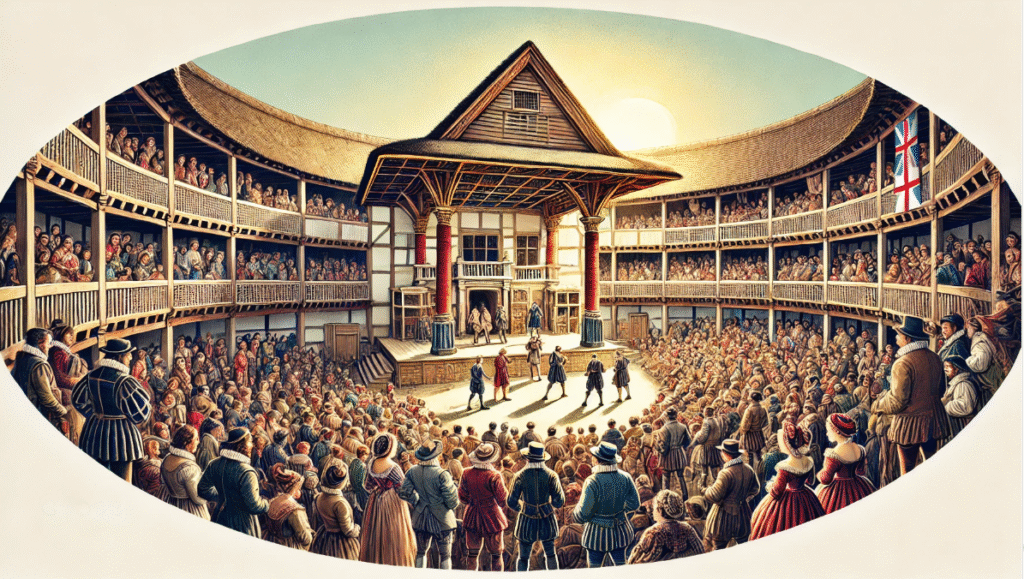
Shakespeare and the Rise of Public Theatre: How His Plays Shaped the Birth of Modern Stage Performances
Imagine sitting in a crowded theatre, the lights dim, the excitement palpable. The actors take their places, and suddenly, you’re transported to another world—one where love, ambition, and betrayal unfold before your eyes. 🎭 But what if I told you that the theatre experience you enjoy today owes much of its existence to one man—William Shakespeare?
Shakespeare and the rise of public theatre weren’t just about great plays; they marked the beginning of a dramatic shift in how theatre was experienced. Before Shakespeare’s influence, theatre was often reserved for the elite or the church. Shakespeare revolutionized this, making it accessible to the masses and shaping the very foundation of modern stage performances.
Table of Contents
Toggle1: The State of Theatre Before Shakespeare
Before Shakespeare’s influence reshaped the theatre world, the landscape of drama was vastly different. Theatre in England had deep roots in religious rituals and courtly performances. It wasn’t until Shakespeare’s era that theatre truly became accessible to the masses. Let’s take a look at the key elements of theatre before Shakespeare made his mark.
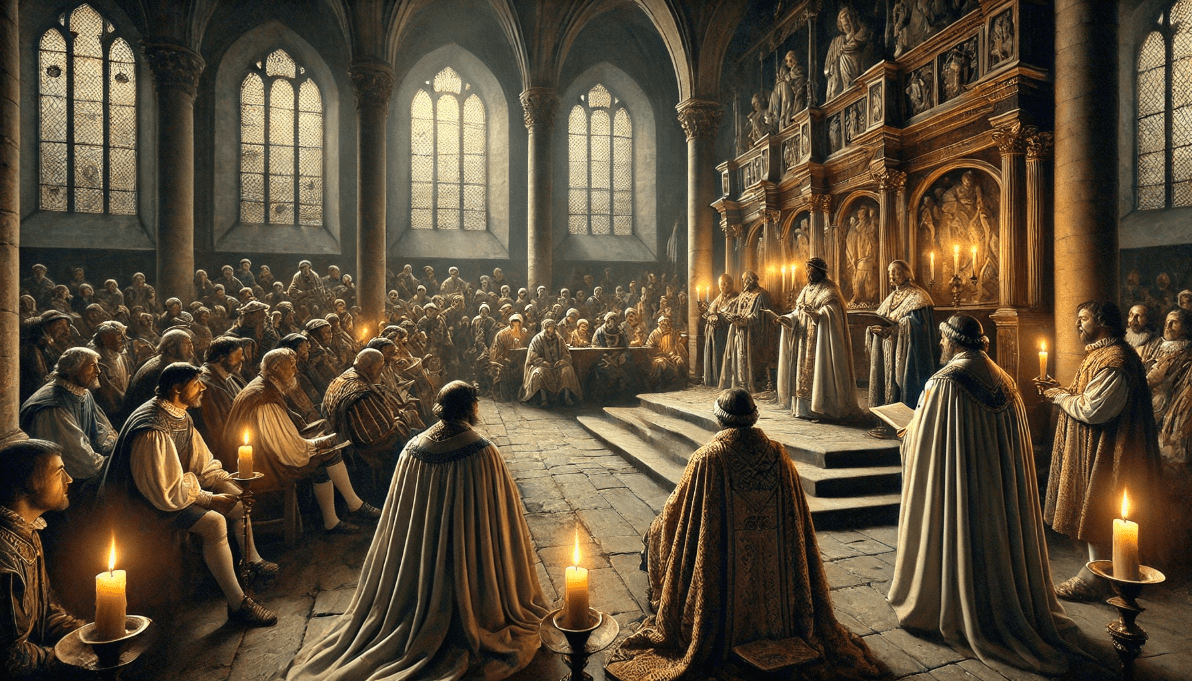
1.1 Religious and Court-Based Performances ⛪
Early English theatre was primarily shaped by religious influences. Mystery plays, which depicted biblical stories, were common in medieval times. These performances were often held in churches or public squares, with actors portraying religious figures to convey moral lessons. However, these performances were limited to religious content and catered mainly to local communities.
Theatre was also reserved for royal courts, where performances were often lavish affairs staged for the elite. These courtly plays were a form of entertainment for kings, queens, and nobles—unlike today, where anyone can attend a theatre performance, these plays were often inaccessible to the common folk.
1.2 A Shift in Audience and Interests 🎭
As society evolved, so did the demand for entertainment. By the late 16th century, England’s population was growing, and the rise of a middle class with more disposable income led to increased demand for public entertainment. People wanted more than just religious or courtly performances—they craved variety, new stories, and immersive experiences that spoke to their daily lives.
This shift in audience interests began to change the way plays were created and performed. The stage was no longer solely a space for royalty; the common people wanted in, and the demand for more accessible theatre grew stronger.
1.3 Limitations of Traditional Theatre
Traditional theatre had its limitations. Plays were often performed in cramped, indoor spaces with no real distinction between the audience and the actors. This setup didn’t foster the same level of interaction or excitement that we associate with modern performances. Furthermore, because theatre was mostly confined to the wealthy or religious circles, the range of topics was narrow—many plays adhered to religious or moralistic themes and avoided exploring more complex human emotions or societal issues.
2: Shakespeare’s Entry into Public Theatre
Shakespeare didn’t just write plays—he revolutionized the entire theatre experience. His entry into public theatre marked a major turning point, transforming the way people engaged with performance art. But how exactly did Shakespeare rise to fame, and how did he help shape the rise of public theatre? Let’s break it down.
2.1 Shakespeare as a Playwright and Actor 🎭

Shakespeare’s journey into public theatre started in the late 16th century when he moved to London, seeking opportunities in the theatre world. At the time, Shakespeare wasn’t just a playwright—he was also an actor. This gave him unique insight into both sides of theatre. As an actor, he understood the needs of performers and could tailor his plays to suit the capabilities of the stage.
His first plays were likely performed at venues like The Theatre and The Curtain, which were popular public playhouses. These theatres were open to all, not just the elite, which gave Shakespeare the opportunity to write plays for a wider audience. His work quickly gained popularity, not only for its rich storytelling but also for its ability to connect with people from all walks of life.
2.2 The Growth of the Globe Theatre 🏛️
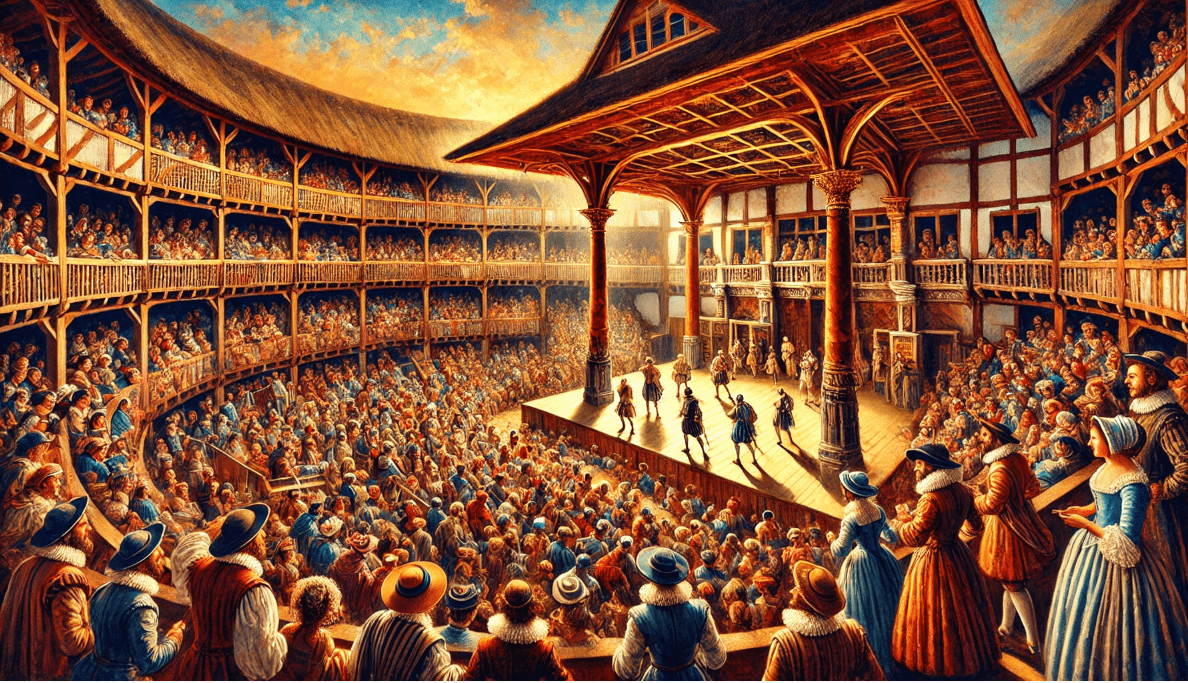
In 1599, Shakespeare co-founded the Globe Theatre, which became a cornerstone of public theatre in London. The Globe was revolutionary for a number of reasons. It was an open-air theatre, allowing audiences to experience plays in a more immersive and natural environment. The design itself—a circular stage with the audience surrounding it—was a stark departure from the enclosed, formal settings of earlier theatres.
The Globe made theatre accessible to the masses. Tickets were inexpensive, and the structure allowed for a wide range of people to attend. For just a penny, the common folk could stand in the “pit” and watch the actors perform. This was a huge step toward democratizing theatre, as it brought together people from different social classes, united by their shared love of drama.
2.3 Public Theatre’s Social Impact 🌍
One of Shakespeare’s greatest achievements was his ability to create theatre that appealed to both the upper and lower classes. At the Globe, you could have a nobleman sitting in a box while a commoner stood right next to them in the pit—both enjoying the same performance. This accessibility fostered a new sense of community around theatre.
Shakespeare’s plays didn’t shy away from important social issues. Whether it was the complexities of power in Macbeth, the role of women in The Taming of the Shrew, or the tensions of social class in The Merchant of Venice, his works were able to spark discussions that resonated with a wide audience. This ability to connect with people from all walks of life was groundbreaking, paving the way for the diverse and inclusive nature of modern public theatre today.
3: The Rise of Modern Stage Performance
Shakespeare didn’t just write plays—he helped to shape the very structure of modern theatre. His influence extended far beyond the words on the page. The way he approached performance, audience interaction, and stage design laid the foundation for the vibrant, inclusive theatre we enjoy today. Let’s explore how Shakespeare played a pivotal role in the rise of modern stage performance.
3.1 The Shift from Private to Public Theatre 🌍
Before Shakespeare, theatre was largely a private affair, confined to royal courts or religious ceremonies. But Shakespeare revolutionized this by bringing performances into the public sphere. The construction of the Globe Theatre in 1599 symbolized this shift. Theatre was now a space for everyone—not just the wealthy elite.
Shakespeare’s plays were written for the masses, appealing to a wide variety of people. The stories were engaging and accessible, touching on universal human experiences—love, betrayal, ambition, and more. This shift meant that public theatre became an essential part of everyday life, attracting a diverse audience from different social classes. As a result, theatre started to be seen as a space for public dialogue and reflection.
3.2 The Influence of Shakespeare on Stage Design 🎭
Shakespeare’s contributions went beyond the words he wrote—his innovative approach to stage design also had a lasting impact on modern theatre. The Globe Theatre was a groundbreaking venue, featuring an open-air design that allowed for dynamic interactions between the actors and the audience. In many ways, it was a precursor to the immersive theatre experiences we have today.
The use of minimal props and a simple stage allowed the focus to remain on the actors and the story. This practice encouraged creativity, as directors and designers had to rely on the actors’ performances and their interaction with the audience to tell the story. Modern theatres, whether they’re small black box spaces or grand Broadway stages, still carry the legacy of Shakespeare’s minimalist approach.
3.3 Audience Engagement: Breaking the Fourth Wall 👁️

One of Shakespeare’s signature contributions to modern theatre was his ability to engage the audience directly. In plays like Hamlet, characters would speak directly to the crowd through soliloquies, creating a sense of intimacy and immediacy. This technique not only made the audience feel involved but also broke down the barrier between actors and spectators.
Today, this “breaking of the fourth wall” remains a core element in theatre. Many modern plays and musicals use direct address, encouraging a deeper connection between the performers and the audience. Shakespeare was one of the first to establish this as a standard feature of stage performances, making the audience feel like active participants in the story.
4: Key Themes in Shakespeare’s Plays That Transcended Time
One of the reasons Shakespeare’s works have endured for centuries is his ability to tap into universal human themes—ones that resonate with people across cultures and eras. These themes are still relevant today and continue to influence storytelling, from theatre to film to literature. Let’s explore some of the key themes in Shakespeare’s plays that have stood the test of time and how they shape modern performances. 🌍
4.1 Universal Human Emotions: Love, Ambition, and Jealousy ❤️💭
Shakespeare’s ability to explore complex human emotions is one of the core reasons his plays remain timeless. Whether it’s the passionate, tragic love in Romeo and Juliet, the overwhelming ambition in Macbeth, or the destructive jealousy in Othello, Shakespeare’s characters reflect the emotions we all experience in real life. These powerful themes connect with audiences on a deep level, making his plays relatable even centuries later.
Practical Insight: Modern playwrights and screenwriters continue to explore these timeless emotions because they touch on the very core of what it means to be human. If you’re looking to create a compelling character, consider how these emotions shape their actions and relationships.
4.2 Power and Corruption: The Dark Side of Leadership 👑
Shakespeare often explored themes of power and its ability to corrupt. In Macbeth, we see how the thirst for power leads to moral decay, while Julius Caesar reflects the complexities of political ambition. These themes speak to the dangers of unchecked authority and the consequences of corrupt leadership.
Why This Matters Today: In today’s world, where political and corporate leaders face scrutiny, Shakespeare’s exploration of power and corruption still rings true. Audiences still find these stories relevant as they watch political dramas or corporate scandals unfold in real life.
4.3 Identity and Self-Discovery: Who Are We, Really? 🤔
Many of Shakespeare’s plays deal with characters questioning their identity and seeking self-discovery. In Hamlet, the famous soliloquy “To be or not to be” explores the complexity of existence. In Twelfth Night, mistaken identities and cross-dressing highlight how identity can be fluid and often shaped by societal expectations.
Practical Insight: Exploring identity is a key theme in many contemporary stories. Whether in personal dramas or fantasy tales, characters who wrestle with who they are or how they fit into the world still capture our attention. This theme provides a rich ground for modern playwrights to explore issues of gender, class, and self-worth.
4.4 Social Class and Inequality: Challenging the Status Quo 💡
Social hierarchy and class differences are recurring themes in Shakespeare’s plays. In The Merchant of Venice, characters struggle with issues of social status and discrimination. In King Lear, we see how family dynamics can mirror the rigid class structure of society. Shakespeare often used his plays to challenge the idea of a fixed social order.
Why It’s Still Relevant: Themes of inequality, discrimination, and the desire to break free from societal constraints are still powerful topics today. From modern dramas addressing racial and class issues to films that question societal norms, Shakespeare’s examination of social class continues to be reflected in today’s performances.
4.5 Fate vs. Free Will: Who Controls Our Destiny? ⚖️
In plays like Macbeth and Romeo and Juliet, Shakespeare delves into the conflict between fate and personal choice. Do we control our destiny, or is it shaped by forces beyond our control? These existential questions make for compelling drama and are themes that continue to captivate audiences.
Why This Matters Today: In an age where people face more choices than ever before, Shakespeare’s exploration of fate and free will is still deeply relevant. Whether in political narratives or personal dramas, audiences are still drawn to stories that question the role of destiny in shaping lives.
5: How Shakespeare Influenced Modern Theatre Formats
Shakespeare’s impact on theatre extends far beyond his own time. His innovative approach to storytelling, stage design, and audience interaction laid the groundwork for many of the theatre formats we enjoy today. From musicals to experimental theatre, Shakespeare’s influence is still felt. Let’s dive into how his contributions shaped the modern theatre world. 🎭
5.1 The Rise of New Theatre Forms 🎤
Shakespeare’s blending of different genres—comedy, tragedy, and history—opened the door for more experimental theatre forms. His ability to shift between light-hearted comedy and intense drama created a framework for the musical theatre format we know today. Musicals, like Les Misérables and Hamilton, combine song, dance, and dialogue to create a dynamic storytelling experience, much like how Shakespeare mixed verse and action.
Practical Insight: Modern playwrights draw on Shakespeare’s genre-blending to create stories that entertain and evoke emotion. Whether through musicals or modern plays, Shakespeare’s ability to entertain through multiple forms continues to influence how stories are told on stage.
5.2 The Impact on Film and Adaptations 🎬
Shakespeare’s influence isn’t confined to the stage. His stories have been adapted countless times for film and television. Movies like West Side Story (a modern adaptation of Romeo and Juliet) and The Lion King (inspired by Hamlet) prove that Shakespeare’s themes and characters transcend time and medium.
Why This Matters Today: Shakespeare’s themes—love, betrayal, power, and destiny—are universal. Filmmakers still use his work as a blueprint for compelling narratives. If you’re a creator looking to tell powerful stories, you can draw inspiration from Shakespeare’s timeless exploration of human nature.
5.3 The Evolution of Immersive Theatre 🎟️
One of the most exciting developments in modern theatre is immersive theatre, where the audience is physically part of the performance. Shakespeare’s interactive performances at the Globe Theatre were early examples of this concept. The Globe’s design, where the audience surrounded the stage, encouraged a level of engagement that made the performance feel immediate and real.
Why This Matters: Today’s immersive theatre experiences, like Sleep No More and Then She Fell, owe a lot to Shakespeare’s ability to engage his audiences directly. His theatrical techniques—like breaking the fourth wall—are still used to draw the audience into the world of the play.
5.4 Shakespeare and the Rise of Experimental Theatre 🎭
Shakespeare was never afraid to experiment with structure and form. His use of soliloquies, multiple plots, and complex characters set the stage for the experimental theatre movement. Today, experimental theatre pushes the boundaries of traditional narrative and performance, with plays like The Wooster Group challenging the audience’s expectations and breaking conventions.
Why This Matters: If you’re an aspiring playwright or director, studying Shakespeare’s willingness to challenge norms will help you push the envelope in your own work. His freedom with form encourages modern artists to break away from traditional structures and experiment with what theatre can be.
6: Practical Takeaways: What Modern Theatre Can Learn From Shakespeare
Shakespeare’s influence on theatre is undeniable, but what can modern theatre artists—whether directors, playwrights, or actors—learn from his approach? Let’s explore some practical takeaways that can elevate contemporary theatre practices, inspired by the Bard himself. 🎭
6.1 Embrace Accessibility and Inclusivity 🎟️
One of Shakespeare’s greatest contributions was making theatre accessible to all. At the Globe Theatre, people from different social backgrounds—rich and poor—sat side by side, enjoying the same performance. Modern theatre can take a page from Shakespeare’s book by embracing inclusivity. Whether through affordable tickets, diverse casting, or creating welcoming spaces for all audiences, accessibility is key to broadening the theatre’s reach.
Actionable Insight: To build a more inclusive theatre experience, consider how your productions can be made more accessible. This could involve creating low-cost ticket options, reaching out to underrepresented communities, or ensuring diverse representation in casting and creative teams.
6.2 Engage Your Audience 💬
Shakespeare’s ability to break the “fourth wall” and engage directly with the audience was revolutionary. His characters spoke directly to spectators, making them feel involved in the action. Modern theatre can benefit from this audience engagement by creating more interactive experiences, whether through breaking the fourth wall, using immersive elements, or fostering a connection between the performers and the crowd.
Actionable Insight: Don’t be afraid to create moments that invite audience interaction. This could be as simple as having actors address the crowd or as immersive as inviting spectators to join the performance itself.
6.3 Experiment with Structure and Form 🎭
Shakespeare’s works were groundbreaking not just for their themes but for their structure. He wasn’t afraid to mix genres, switch between comedy and tragedy, or break traditional rules. Modern theatre can take inspiration from Shakespeare’s experimentation with form by embracing creative storytelling techniques. This might include non-linear narratives, unconventional staging, or blending different media (like film and theatre).
Actionable Insight: Experiment with different styles and structures in your next production. Try mixing genres or incorporating multimedia elements to offer a fresh, innovative experience for your audience.
6.4 Explore Timeless Themes 🌍

Shakespeare’s plays resonate with audiences because they explore timeless themes—love, power, betrayal, and identity. These are themes that continue to captivate audiences, regardless of era. Modern theatre can benefit from diving deep into these universal human experiences, exploring them through a contemporary lens.
Actionable Insight: Think about how timeless themes like love, ambition, or justice can be explored in your own work. Consider how modern issues and social changes can shed new light on classic themes, making them more relevant to today’s audiences.
6.5 Prioritize Character Depth and Development 💡
Shakespeare’s characters are among the most complex in literature. From the conflicted Hamlet to the ambitious Lady Macbeth, his characters felt real because they were multi-dimensional. Modern theatre should strive to create characters that feel just as rich and complex, allowing actors to explore deep emotional landscapes.
Actionable Insight: When writing or directing, focus on creating characters with depth. Give them flaws, desires, and motivations that make them feel fully realized. A well-crafted character is often the heart of a successful production.
Shakespeare’s influence on theatre is both profound and enduring. His ability to transform theatre into a public, inclusive experience, his mastery of universal themes, and his innovative approach to stage design and audience engagement continue to shape how we experience live performance today. From the Globe Theatre’s inclusive atmosphere to the immersive, genre-blending productions we see now, Shakespeare set the stage for modern theatre as we know it. 🎭
By embracing his lessons—prioritizing accessibility, engaging audiences, experimenting with form, and exploring timeless themes—we can continue to evolve and enrich the world of theatre. Whether you’re a playwright, actor, director, or theatre enthusiast, understanding Shakespeare’s impact can inspire a deeper connection with the art form and help create performances that resonate across generations.
Shakespeare didn’t just create plays; he created a lasting legacy that continues to inspire theatre practitioners around the world. So, the next time you step into a theatre, whether it’s a Broadway show, an immersive experience, or a local performance, remember that you’re part of a tradition that began with the Bard. 🌟
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How did Shakespeare contribute to the rise of public theatre?
Shakespeare played a pivotal role in making theatre accessible to the general public. He helped move performances away from royal courts and church settings to public venues like the Globe Theatre, where people from all social classes could enjoy his plays. His works appealed to both the elite and the common folk, creating a more inclusive theatre culture.
2. Why is the Globe Theatre important in Shakespeare's legacy?
The Globe Theatre is significant because it symbolized the shift toward public, accessible theatre. It was an open-air venue that welcomed a wide range of people, with affordable ticket options for the general public. Shakespeare’s association with the Globe made theatre a communal experience, breaking down social barriers in entertainment.
3. What themes in Shakespeare's plays are still relevant today?
Shakespeare’s exploration of universal themes like love, ambition, power, jealousy, and identity continues to resonate with modern audiences. These themes address deep human emotions and societal issues that remain relevant across time, making his plays timeless and applicable to today’s world.
4. How did Shakespeare change the way plays were performed?
Shakespeare revolutionized the way plays were performed by introducing dynamic stage designs, minimalist sets, and breaking the fourth wall. His innovative approach, which emphasized actor-audience interaction, paved the way for modern stage techniques and immersive experiences seen in today’s theatre productions.
5. What impact did Shakespeare have on modern theatre formats like musicals?
Shakespeare’s blending of genres—comedy, tragedy, and history—laid the groundwork for the multi-genre approach seen in modern theatre formats like musicals. His ability to mix various forms of storytelling, including dialogue and verse, influenced the creative structure of musical theatre, where songs and dialogue often coexist to tell a story.
6. How did Shakespeare's use of language influence modern theatre?
Shakespeare’s mastery of language, including his inventive use of metaphors, soliloquies, and wordplay, has influenced modern theatre by encouraging more dynamic, poetic dialogue. Contemporary playwrights still draw on his techniques to create powerful, emotional connections with audiences through language.
7. What can modern playwrights learn from Shakespeare's work?
Modern playwrights can learn from Shakespeare’s ability to blend entertainment with deep societal commentary. His focus on character development, universal themes, and audience engagement remains a timeless strategy for creating compelling stories that resonate with a wide audience.
8. How did Shakespeare's public theatre appeal to all social classes?
Shakespeare’s public theatre was inclusive, offering performances that appealed to both the wealthy and the working class. The Globe Theatre had affordable standing spots for commoners, while wealthier patrons could sit in more comfortable, private areas. This setup made theatre a shared experience across social divides, democratizing the art form.
