The Elizabethan era, named after Queen Elizabeth I who ruled England from 1558 to 1603, was a time of immense cultural, political, and economic growth in England. It was a period marked by the flourishing of the arts, including the works of playwrights like The influence of Elizabethan exploration on Shakespeare, as well as the expansion of England’s global influence through exploration and colonization. Shakespeare, often considered the greatest playwright in the English language, was a product of the Elizabethan era. The influence of Elizabethan exploration on Shakespeare, including plays like “Hamlet,” “Macbeth,” and “Romeo and Juliet,” continue to be studied and performed around the world.
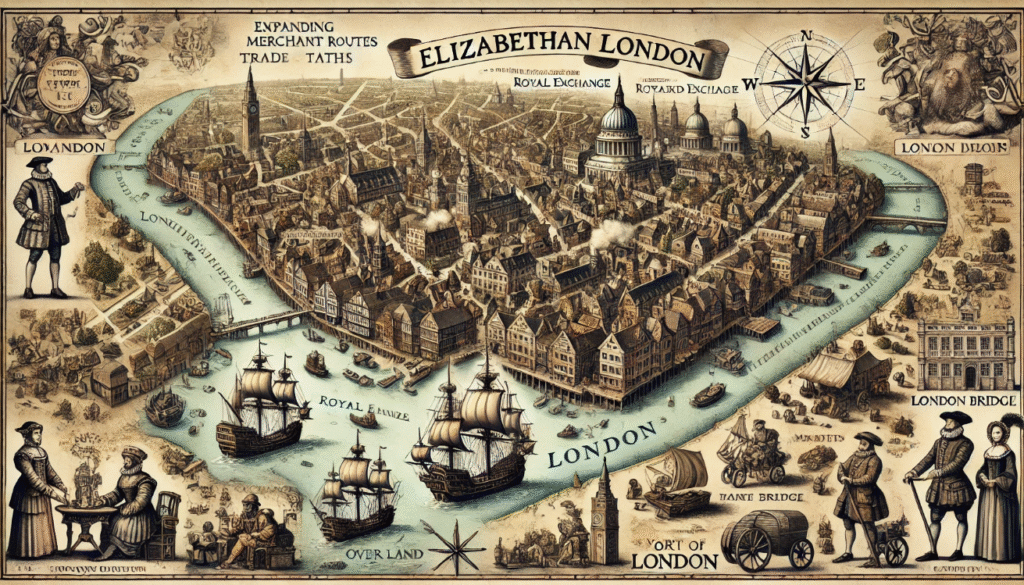
The Elizabethan Age of Exploration

During the reign of the influence of Elizabethan exploration on Shakespeare, global exploration and discoveries were at the forefront of European expansion. Key figures such as Sir Francis Drake and Walter Raleigh led English voyages to the New World, seeking new trade routes and establishing colonies. These explorations had a profound impact on England and Europe, leading to cultural encounters and the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. The establishment of new trade routes and colonies brought wealth and new possibilities to England and Europe, influencing art, literature, and the economy. The influence of Elizabethan exploration on Shakespeare encounters with new cultures also led to the exchange of ideas and the enriching of European society. This era of exploration opened the world to new opportunities and greatly influenced the development of the modern world.
Shakespeare’s World and Influences
During Shakespeare’s lifetime, which spanned from 1564 to 1616, England experienced a period of great exploration and expansion. This was known as the Elizabethan era, named after Queen Elizabeth I, and it was a time when English sailors like Sir Francis Drake and Sir Walter Raleigh were venturing to distant lands and bringing back new ideas and exotic goods. This era of exploration had a significant impact on Elizabethan theater, as playwrights like Shakespeare were inspired by the stories and cultures of these newly discovered lands. This influence can be seen in plays like “The Tempest” and “Othello,” which incorporate themes of travel, foreign cultures, and the clash of civilizations.
Shakespeare’s writing was undoubtedly influenced by the intellectual atmosphere of his time and his own personal experiences. Growing up in Elizabethan England, he would have been surrounded by the great thinkers and writers of the Renaissance, such as Sir Francis Bacon and Christopher Marlowe. These influences can be seen in his works, which often explore complex philosophical and moral questions. Additionally, Shakespeare’s own experiences would have shaped his writing. His upbringing in a middle-class family and his eventual rise to prominence in the London theater scene would have given him a unique perspective on social class and power dynamics, which are recurring themes in his plays.
Themes of Exploration in Shakespeare’s Plays
New Worlds and Encounters:
Shakespeare’s plays that involve exploration or unfamiliar lands, such as The Tempest, The Winter’s Tale, and Twelfth Night, often depict characters encountering new cultures, landscapes, and ways of life. These plays explore themes of discovery and cultural exchange as characters navigate the unknown and interact with people and places that are different from their own. The exploration of unfamiliar lands in these plays serves as a backdrop for the characters’ personal growth and the development of their relationships, as they navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by their encounters with the unknown. Overall, these plays offer a rich and complex exploration of the human experience in the context of exploration and cultural exchange.
Colonialism and Conquest:

Exploration during the age of imperialism and colonization often involved the subjugation and exploitation of indigenous peoples. This power dynamic is reflected in plays like The Tempest, where Caliban’s character serves as a symbol of the colonized. The ethical implications of this power dynamic raise important questions about the impact of colonization on indigenous cultures and the responsibility of the colonizers to acknowledge and address the harm caused. It also prompts discussions about the lasting effects of imperialism on global power dynamics and the continuing struggles for decolonization and social justice.
The Human Condition and Exploration:

Shakespeare’s exploration of human nature through journeys to new lands, both internal and external, is a recurring theme in many of his plays. The physical voyages depicted in his works often mirror the emotional or psychological journeys of the characters. These journeys allow Shakespeare to delve into the complexities of human nature, showcasing the inner turmoil, growth, and transformation experienced by his characters as they navigate the challenges of new environments and circumstances. This exploration of human nature through the lens of physical and emotional journeys adds depth and richness to Shakespeare’s storytelling, making his works enduring and relatable to audiences across time and cultures.
Shakespeare’s Use of Exotic Settings and Foreign Cultures

Exploration of plays set in foreign or far-off lands (e.g., Othello set in Venice and Cyprus, The Merchant of Venice, The Tempest).
The portrayal of non-English cultures and how Shakespeare used them to reflect on themes of identity, power, and conflict.
The impact of the fascination with the “exotic” in Elizabethan England and Shakespeare’s use of these elements in storytelling.
Shakespeare’s Representation of Discovery and Adventure

In Shakespeare’s works, adventure, discovery, and new territories are often portrayed as transformative experiences for the characters. These themes are woven throughout many of his plays, including A Midsummer Night’s Dream and Pericles. In A Midsummer Night’s Dream, the characters embark on a journey into the mystical forest, where they encounter magical creatures and experience personal growth. This journey represents a departure from the constraints of the civilized world and allows the characters to explore their true desires and emotions. Similarly, in Pericles, the titular character embarks on a series of adventures across the Mediterranean, encountering new cultures and facing numerous challenges along the way.
Exploration in Shakespeare’s works often serves as a metaphor for the pursuit of knowledge or self-discovery. Characters embark on physical journeys that mirror their internal quests for understanding and enlightenment. Through exploration, they encounter new experiences, confront their fears, and ultimately grow as individuals. This theme is integral to Shakespeare’s broader narrative arc, as it reflects the universal human desire for personal and intellectual exploration.
The Legacy of Elizabethan Exploration in Shakespeare’s Work

Exploration during Shakespeare’s time greatly influenced the structure and themes of his writing. The age of exploration brought new ideas, cultures, and experiences to England, which Shakespeare incorporated into his plays. This exposure to different cultures and perspectives expanded his imagination and allowed him to create more diverse and complex characters and settings. Additionally, the themes of exploration, adventure, and discovery often appeared in his works, reflecting the spirit of the time. Overall, exploration left an indelible mark on Shakespeare’s writing, enriching his works with a broader understanding of the world and human experience.
Shakespeare’s influence on how later writers and artists depicted exploration, conquest, and cultural exchange is undeniable. His works, such as “The Tempest” and “Othello,” have shaped the way these themes are portrayed in literature and theater. His nuanced exploration of the complexities of conquest and cultural exchange has set a standard for later works to follow. These themes remain relevant in modern literature and theater as they continue to reflect the complexities of human interaction and the impact of exploration and conquest on both the conquerors and the conquered. The ongoing relevance of these themes is evident in the way contemporary writers and artists continue to grapple with the consequences of cultural exchange and conquest in their works.
The Elizabethan Age of Exploration had a significant influence on Shakespeare’s writing. The exploration of new worlds, encounters with different cultures, and the discovery of new lands had a profound impact on the societal, political, and cultural landscape of the time. This era of exploration sparked a sense of curiosity and wonder about the world beyond England’s shores, which is reflected in Shakespeare’s plays through the exploration of new settings, characters, and themes. Shakespeare’s exploration of new worlds through his plays mirrors the societal, political, and cultural transformations of his time. His works often depict the clash of different cultures, the consequences of colonization, and the complexities of navigating uncharted territories.